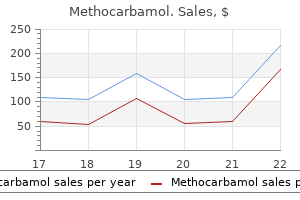
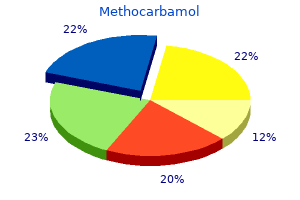
Buy methocarbamol 500 mg with mastercard
Lineage commitment of skeletal precursor cells to chondrocytes and osteoblasts is set by catenin levels spasms under left breastbone 500 mg methocarbamol cheap overnight delivery. From top to bottom: mesenchymal cells (blue) spasms constipation 500 mg methocarbamol cheap otc, resting and proliferating (nonhypertrophic) chondrocytes (red), and hypertrophic chondrocytes (yellow). Lines with arrowheads point out a constructive action, and lines with bars indicate an inhibition. The trabeculae of bone are being shaped by the osteoblasts lining their surface (arrows). Osteocytes are trapped in lacunae (arrowheads), and primordial osteons are starting to kind. Histogenesis of Cartilage Cartilage develops from mesenchyme through the fifth week. In areas the place cartilage is programmed to develop, the mesenchyme condenses to form chondrification facilities. The mesenchymal cells differentiate into prechondrocytes and then into chondroblasts, which secrete collagenous fibrils and ground substance (extracellular matrix). Subsequently, collagenous or elastic fibers, or each, are deposited in the intercellular substance or matrix. Precursor cells differentiate into osteoblasts (boneforming cells) and start to deposit unmineralized matrix (osteoid). Concentric lamellae develop round blood vessels, forming osteons (Haversian systems). Some osteoblasts stay on the periphery of the growing bone and continue to lay down lamellae, forming plates of compact bone on the surfaces. This spongy surroundings is considerably accentuated by the motion of cells (osteoclasts) that reabsorb bone. In the interstices of spongy bone, the mesenchyme differentiates into bone marrow. Like cartilage, bone consists of cells and an natural intercellular substance (bone matrix) that contains collagen fibrils embedded in an amorphous component. In a protracted bone, for Cartilage Model of Bone instance, the first center of ossification appears within the diaphysis (part of an extended bone between its ends), which types the shaft of a bone. At this middle of ossification, chondrocytes (cartilage cells) increase in dimension (hypertrophy), the matrix turns into calcified, and the cells die. Concurrently, a skinny layer of bone is deposited beneath the perichondrium surrounding the diaphysis, and the Calcified cartilage Cartilage Mesenchymal cell Perichondrium Bone Arteries Intracartilaginous Ossification Epiphyseal artery Enlarged area Chondroblast Cartilage matrix A Diaphyseal (primary) heart of ossification Uncalcified hyaline cartilage Epiphyseal cartilage plate Calcified hyaline cartilage Chondrocyte Periosteum Periosteal capillary Subperiosteal bone Metaphyseal artery B Nutrient artery Medullary cavity of lengthy bone Epiphyseal (secondary) center of ossification Epiphyseal artery Epiphysis Nutrient artery Diaphysis Epiphysis C lengthy bone. Invasion by vascular connective tissue from blood vessels surrounding the periosteum also breaks up the cartilage. Some invading cells differentiate into hemopoietic cells (blood cells of bone marrow). Toward the diaphysis, the cartilage cells hypertrophy (increase in size), and the matrix turns into calcified. Bone is deposited on these spicules by osteoblasts; resorption of the bone retains the spongy bone plenty comparatively constant in size and enlarges the medullary cavity. Ossification of limb bones begins on the finish of the embryonic interval (56 days after fertilization). Pregnant women are advised to keep an sufficient consumption of those parts to protect wholesome bones and enamel. At start, the diaphyses are largely ossified, however a lot of the epiphyses are still cartilaginous. Secondary ossification facilities appear in the epiphyses in most bones in the course of the first few years after start. On completion of development, the cartilage plate is changed by spongy bone, the epiphyses and diaphysis are united, and no further elongation of the bone occurs. The price of deposition and resorption is balanced to regulate the thickness of the compact bone and the scale of the medullary cavity. The improvement of irregular bones is much like that of the epiphyses of long bones. Joints with little or no motion are categorized based on the kind of materials holding the bones together; for instance, the bones of fibrous joints are joined by fibrous tissue. Hereditary vitamin D� resistant rickets results from mutations within the vitamin D receptor. This primordial joint might differentiate right into a synovial joint (B), a cartilaginous joint (C), or a fibrous joint (D). Cartilaginous Joints During the event of cartilaginous joints, the interzonal mesenchyme between the growing bones differentiates into hyaline cartilage. Centrally, the mesenchyme disappears, and the resulting area turns into the joint cavity (synovial cavity). Each sclerotome consists of loosely organized cells cranially and densely packed cells caudally. The remaining densely packed cells fuse with the loosely arranged cells of the immediately caudal sclerotome to form the mesenchymal centrum, the primordium of the body of a vertebra. Thus, every centrum develops from two adjoining sclerotomes and turns into an intersegmental construction. The nerves lie near the intervertebral discs, and the intersegmental arteries lie on all sides of the vertebral bodies. In the thorax, the dorsal intersegmental arteries turn out to be the intercostal arteries. This nucleus is later surrounded by circularly arranged fibers that kind the annulus fibrosus. The mesenchymal cells in the body wall kind costal processes, which type the ribs in the thoracic area. Probably because of joint actions, the mesenchymal cells subsequently disappear from the surfaces of the articular cartilages. An abnormal intrauterine environment limiting embryonic and fetal movements may intrude with limb growth and trigger joint fixation. Approximately one third of those slow-growing malignant tumors occurs on the base of the cranium and extends to the nasopharynx. Surgical resection has offered long-term, disease-free survival for many patients. This positional change of the sclerotomal cells is effected by differential progress of the encircling structures and never by active migration of sclerotomal cells. The two facilities in every centrum fuse at the end of the embryonic period to form a cartilaginous centrum. Concomitantly, the centers in the neural arches fuse with one another and the centrum. The spinous and transverse processes develop from extensions of chondrification facilities within the neural arch. Bony Stage of Vertebral Development Ossification of typical vertebrae begins in the course of the seventh week and ends by the twenty fifth 12 months.
Purchase methocarbamol 500 mg mastercard
This leads to a persistent connection of variable lengths between these usually separated structures muscle relaxant safe in pregnancy methocarbamol 500 mg with mastercard, or laryngotracheoesophageal cleft muscle relaxant walgreens purchase 500 mg methocarbamol with amex. Note the air current within the distal gastrointestinal tract, indicating the presence of the tracheoesophageal fistula. The outgrowth might terminate in normal-appearing lung tissue, forming a tracheal lobe of the lung. This diverticulum could trigger recurrent an infection and respiratory distress in infants. Together with the surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, the bronchial buds differentiate into bronchi and their ramifications within the lungs. The embryonic proper major bronchus is slightly bigger than the left one and is oriented more vertically. This relationship persists within the grownup; consequently, a overseas body is extra prone to enter the right major bronchus than the left one. On the proper, the superior lobar bronchus will supply the higher (superior) lobe of the lung, whereas the inferior bronchus subdivides into two bronchi, one to the middle lobe of the right lung and the other to the lower (inferior) lobe. On the left, the two secondary bronchi supply the higher and decrease lobes of the lung. The segmental bronchi, 10 in the best lung and eight or 9 within the left lung, begin to kind by the seventh week. The segmental bronchi, with the encircling mass of mesenchyme, form the primordia of the bronchopulmonary segments. As the bronchi develop, cartilaginous plates develop from the surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme. The bronchial easy muscle and connective tissue and the pulmonary connective tissue and capillaries are additionally derived from this mesenchyme. With enlargement, the lungs and pleural cavities grow caudally into the mesenchyme of the physique wall and soon lie close to the heart. By 16 weeks, all major elements of the lung have formed, besides these involved with fuel trade. Maturation of Lungs Maturation of the lungs is split into four histologic levels: the pseudoglandular, canalicular, terminal sac, and alveolar phases. Canalicular Stage (16 to 25 Weeks) the canalicular stage overlaps the pseudoglandular stage as a end result of cranial segments of the lungs mature quicker than caudal ones. By 24 weeks, every terminal bronchiole has formed two or extra respiratory bronchioles, each of which divides into three to six passages, the primordial alveolar ducts. Respiration is possible at the finish of the canalicular stage (26 weeks) because some thin-walled terminal sacs (primordial alveoli) have developed at the ends of the respiratory bronchioles and lung tissue is properly vascularized. Although a fetus born toward the top of this period could survive if given intensive care, this untimely neonate might die as a result of its respiratory and different systems are still relatively immature. C and D, Note that the alveolocapillary membrane is skinny and that some capillaries bulge into the terminal sacs and alveoli. At 26 weeks, the terminal sacs are lined mainly by squamous epithelial cells of endodermal origin, kind I pneumocytes, across which gasoline exchange occurs. Surfactant varieties as a monomolecular movie over the internal walls of the alveolar sacs and counteracts surface tension forces at the air-alveolar interface. This facilitates enlargement of the terminal sacs by stopping atelectasis (collapse of sacs during exhalation). The production of surfactant will increase in the course of the terminal phases of being pregnant, particularly over the last 2 weeks. By 26 to 28 weeks, the fetus normally weighs approximately 1000 g and sufficient alveolar sacs and surfactant are present to permit survival of a prematurely born infant. Before this, the lungs are normally incapable of providing enough fuel change, partly because the alveolar floor space is inadequate and the vascularity underdeveloped. Fetuses born at 24 to 26 weeks after fertilization might survive if given intensive care; however, they could suffer from respiratory misery due to surfactant deficiency. Survival of these infants has improved with the utilization of antenatal corticosteroids (steroids produced by the adrenal cortex), which induces surfactant production, and likewise with postnatal surfactant replacement therapy. Observe the thin-walled terminal sacs (primordial alveoli) that have developed at the ends of the respiratory bronchioles. Also observe that the numbers of capillaries have increased and that a few of them are intently associated with the creating alveoli. By the late fetal period (38 weeks), the lungs are capable of respiration because the alveolocapillary membrane (pulmonary diffusion barrier or respiratory membrane) is sufficiently thin to enable gas change. At the start of the alveolar stage (32 weeks), each respiratory bronchiole terminates in a cluster of thinwalled alveolar sacs, separated from one another by free connective tissue. The transition from dependence on the placenta for fuel trade to autonomous gasoline trade requires the following adaptive adjustments within the lungs: Production of surfactant within the alveolar sacs Transformation of the lungs from secretory organs into organs capable of gas trade Establishment of parallel pulmonary and systemic circulations Approximately 95% of mature alveoli develop postnatally. Alveolar growth is largely completed by 3 years of age, however new alveoli are added till approximately eight years of age. Unlike mature alveoli, immature alveoli have the potential for forming extra primordial alveoli. The main mechanism for growing the number of alveoli is the formation of secondary connective tissue septa that subdivide present primordial alveoli. Lung development in the course of the first few months after start is characterized by an exponential improve within the floor area of the air�blood barrier via the multiplication of alveoli and capillaries. Approximately 150 million primordial alveoli, one half of the grownup quantity, are current in the lungs of a full-term neonate. On chest radiographs, therefore, the lungs of neonates are denser than adult lungs. Between the third and eighth years, the grownup complement of 300 million alveoli is achieved. Molecular research indicate that lung improvement is managed by a cascade of signaling pathways that are regulated by the temporal and sequential expression of extremely conserved genes. Fibroblast progress factor 10 and other signals from splanchnic mesenchyme most likely induce the outgrowth of the respiratory buds. Branching of the buds (branching morphogenesis, or production) and its proliferation rely upon epithelial (endodermal foregut)�mesenchymal (mesoderm) interactions. The Wnt signaling pathway performs an essential function in the inductive interactions between epithelium and mesenchyme. The patterning morphogen sonic hedgehog (Shh-Gli) modulates the expression of fibroblast growth factor 10, which controls the branching of the bronchial buds. Also, the morphogen retinoic acid regulates Hox a5, b5, and c4, which are expressed within the creating lung. By birth, the fetus has had the benefit of a number of months of respiration exercise. In addition, these movements stimulate lung growth, presumably by making a stress gradient between the lungs and the amniotic fluid. At start, the lungs are approximately half full of fluid derived from the amniotic cavity, lungs, and tracheal glands. The lungs are underinflated and the alveoli include a fluid with a excessive protein content material that resembles a glassy, or hyaline, membrane. This membrane is believed to be derived from a mix of substances in the circulation and from the injured pulmonary epithelium.
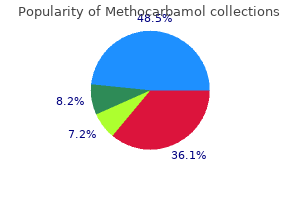
500 mg methocarbamol buy
Lu Z xanax muscle relaxer discount methocarbamol 500 mg, MacKinnon R: Electrostatic tuning of Mg2+ affinity in an inward-rectifier K+ channel spasms lower back methocarbamol 500 mg purchase without prescription. Muto S, Tsuruoka S, Miyata Y, et al: Basolateral Na+/H+ change maintains potassium secretion throughout diminished sodium transport within the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Lesage F, Lazdunski M: Molecular and functional properties of two-pore-domain potassium channels. Muto S, Sansom S, Giebisch G: Effects of a excessive potassium food regimen on electrical properties of cortical accumulating ducts from adrenalectomized rabbits. Najjar F, Zhou H, Morimoto T, et al: Dietary K+ regulates apical membrane expression of maxi-K channels in rabbit cortical amassing duct. Babilonia E, Wei Y, Sterling H, et al: Superoxide anions are concerned in mediating the impact of low K intake on c-Src expression and renal K secretion in the cortical collecting duct. The Regulation of Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate Excretion by the Kidney Theresa J. The molecular processes answerable for the reabsorption of these substances by the kidney and the localization of the cognate molecular machinery alongside the nephron are unique for calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium. In the case of calcium and phosphorus, similar hormones regulate the efficiency of renal reabsorption, although particular components for every substance additionally operate to regulate reabsorption. With magnesium, the molecular mediators of reabsorption are poorly regulated, and the exact hormonal factors involved within the regulation of magnesium reabsorption by the nephron are much less well outlined. Several biochemical and physiologic processes, including nerve conduction and function, coagulation, enzyme activity, exocytosis, and bone mineralization, are critically depending on regular calcium concentrations in extracellular fluid. Following absorption within the intestine, calcium in the extracellular fluid area is deposited in bone (the major repository of calcium in the body) and is filtered within the kidney. The concentration of calcium in serum varies with age and gender, with larger values being present in children and adolescent subjects than in adults. CaProt, Protein-bound calcium; CaR, diffusible calcium complexes; Ca2+, ionized calcium. An equation defining the amount of calcium (mmol/L) bound to albumin and globulins (g/L) as a function of pH is as follows12: [CaProt] = zero. The change in serum calcium concentration is detected by the parathyroid gland calcium-sensing receptor, a G protein�coupled receptor, which alters parathyroid hormone launch from the parathyroid cell. As a result of reabsorption processes that happen in each the proximal and distal tubules, solely 1% to 2% of calcium filtered on the glomerulus appears in the urine. As famous earlier, about 60% to 70% of total plasma calcium is free (not protein-bound) and is filtered on the glomerulus. Ca2+ permeates via claudin-254 and simultaneously competitively inhibits Na+ conductance. Undefined Ca2+ channels and intracellular Ca2+ binding proteins affect the movement of Ca2+ into and across the cell. The salutary effects of isotonic saline administration in sufferers with hypercalcemia are attributable to a discount in Ca2+ reabsorption because of lowered Na+ reabsorption. This transepithelial voltage supplies the driving force for passive Ca2+ reabsorption via the paracellular pathway. The particular role performed by claudins in the tight junction of the thick ascending limb of Henle in Ca2+ reabsorption (and Mg2+ reabsorption, as discussed in the subsequent section) is controversial. NaCl absorption is diminished, as is potassium recycling, leading to a discount in lumen positivity that drives Ca2+ reabsorption. Indeed, thiazide administration was associated with hypocalciuria in Trpv5 knockout mice. Urinary calcium excretion and renal fractional excretion of calcium are decreased in Sost-/-mice. Clearly, additional work needs to be performed to dissect the proximate drivers of increased sclerostin-mediated renal Ca+ reabsorption. Such information is essential because it suggests how medicine could be designed to inhibit or improve the exercise of those Ca2+ transporters. Residues of transmembrane helices 5 and 6 kind a central pore (black), the place regulated calcium inflow occurs. The yellow floor patches indicate residues that show substantial chemical shifts when calbindin D28K is titrated with three peptides derived from other proteins identified to work together. The A, or actuator area, can additionally be very cellular and actually consists of two subdomains, which can exist to protect the phosphoryl group from hydrolysis and typically block ion access or egress. In plasma, about 70% of Mg is ultrafiltrable, 55% is free, and 14% of Mg is in the form of soluble complexes with citrate and phosphate. When rats203-205 and humans182,206 are placed on Mg-deficient diets, the serum Mg stage decreases inside 1 day in rats and in 5 to 6 days in people. Bone Mg and blood mononuclear cell Mg concentrations correlate well with whole body Mg and serum Mg levels. Absorbed magnesium enters the extracellular fluid pool and strikes out and in of bone and gentle tissues. Approximately 130 mg of magnesium (equivalent to the web quantity absorbed in the intestine) is excreted within the urine. In experimental animals and people, feeding a food regimen low in magnesium leads to a speedy lower in urinary and fecal magnesium and the development of a negative magnesium stability. Because urinary magnesium excretion is about 150 mg/24 hr, a considerable fraction of filtered magnesium is reabsorbed along the tubule (95%). The mobile and molecular mechanisms whereby magnesium is reabsorbed within the proximal nephron are unknown. It is unclear about the mode of exit of magnesium from the cell into the interstitial house. Precisely how these proteins interact with one another to regulate magnesium transport is at present underneath investigation. Where claudin-16 and claudin-19 are coexpressed, linear heteropolymeric fibrils might develop throughout the plasma membrane, as proven (claudin-16, darklight green; claudin-19, blue-cyan), a model based on interactions noticed in the mouse claudin-15 crystal lattice that are conserved in these human claudins. Interacting fibrils may be later modified to obtain differentiation in the barrier operate of these tight junctions. The last two, extra extremely conserved helices and their connecting loop represent the pore. These helices most probably affiliate with the first 4 helices of a neighboring subunit within the homotetramer. The connecting loop for these final two helices in all probability contains a non�membranespanning -helix that may have functional significance. A normal food regimen enough in phosphorus usually contains roughly 1500 mg of phosphorus. Approximately 1100 mg of ingested dietary phosphate is absorbed in the proximal intestine predominantly in the jejunum. About 200 mg of phosphorus is secreted into the intestine through pancreatic and intestinal secretions, giving a web phosphorus absorption of roughly 900 mg/24 hr. Absorbed phosphorus enters the extracellular fluid pool and strikes in and out of bone (and, to a smaller extent, in and out of soppy tissues), as needed (~200 mg). Approximately 900 mg of phosphorus (equivalent to the amount absorbed within the intestine) is excreted within the urine. In human plasma or serum, phosphorus exists in the form of inorganic phosphorus or phosphate (Pi), lipid phosphorus, and phosphoric ester phosphorus.
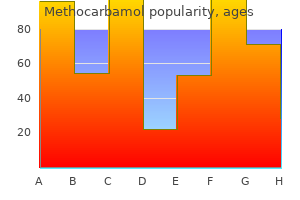
Cheap 500 mg methocarbamol with amex
The total body water deficit in a hyperosmolar patient could be estimated using the next method: Total physique water deficit = zero muscle relaxant drug class 500 mg methocarbamol order. This method relies on three assumptions: (1) complete body water is roughly 60% of the premorbid body weight; (2) no body solute was lost as the hyperosmolality developed; and (3) the premorbid serum [Na+] was a hundred and forty mEq/L spasms right side under ribs methocarbamol 500 mg order online. The intranasal kind is offered as an aqueous answer containing 100 �g/mL in a bottle with a calibrated rhinal tube, which requires specialized training to use appropriately, or as a nasal spray delivering a metered dose of 10 �g in 0. Recently, a sublingual preparation, referred to as Minrin Melt, has been launched in doses of 60 to a hundred and twenty �g. This is equipped as an answer containing 4 �g/mL and may be given by the intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous route. The parenteral kind is approximately 5 to 10 occasions stronger than the intranasal preparation, and the really helpful dosage is 1 to 2 �g each eight to 12 hours. For intranasal and parenteral preparations, increasing the dose typically has the impact of prolonging the period of antidiuresis for several hours quite than growing its magnitude; consequently, altering the dose can be helpful to cut back the required frequency of administration. Hydrochlorothiazide at doses of 50 to a hundred mg/day usually reduces urine output by roughly 50%, and its efficacy could be further enhanced by proscribing sodium consumption. Unless the hypothalamic thirst middle can additionally be affected by the primary lesion causing superimposed osmoreceptor dysfunction, these sufferers will develop thirst when the plasma osmolality increases by only 2% to 3%. Polyuria and polydipsia are thus inconvenient and disruptive, however not life-threatening. However, hypo-osmolality is basically asymptomatic and could additionally be progressive if water consumption continues during a period of steady antidiuresis. Therefore, treatment have to be designed to reduce polyuria and polydipsia but without an undue danger of hyponatremia from overtreatment. Treatment should be individualized to determine optimal dosage and dosing intervals. Having tried each preparations, the patient can then select which they like for long-term utilization. In a few sufferers, the impact of intranasal or oral desmopressin is erratic, probably on account of variable interference with absorption from the gastrointestinal tract or nasal mucosa. This variability can be lowered and the length of action prolonged by administering the drug on an empty stomach239 or after thorough cleaning of the nostrils. Hyponatremia is a uncommon complication of desmopressin therapy; nevertheless, it solely occurs if the affected person is continually antidiuretic whereas maintaining a fluid consumption adequate to turn out to be volume expanded and natriuretic. Thus, the blood glucose degree must first be brought under control to remove an osmotic diuresis as the reason for the polyuria. In addition, extra fluids administered intravenously could additionally be retained perioperatively however then excreted normally postoperatively. However, as a outcome of many neurosurgeons fear water overload and mind edema after this type of surgical procedure, the patient is sometimes treated solely with intravenous fluid alternative for a substantial time before the establishment of antidiuretic hormone therapy (see the potential advantages of this strategy below). However, if the affected person is unable to respond to thirst due to a decreased stage of consciousness or from hypothalamic harm to the thirst heart, fluid steadiness must be maintained by administering fluid intravenously. Postoperatively, desmopressin may be given parenterally in a dose of 1 to 2 �g subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously. A prompt reduction in urine output ought to happen; the length of the antidiuretic effect is mostly 6 to 12 hours. Usually, the affected person is hypernatremic with comparatively dilute urine when therapy is began. One ought to monitor the urine osmolality and urine quantity to be sure that the dose was effective and check the serum [Na+] at frequent intervals to ensure some improvement of hypernatremia. The long-term management of osmoreceptor dysfunction syndromes requires an intensive search for probably treatable causes (see Table sixteen. The success of this regimen ought to be monitored periodically (weekly at first, later every month, relying on the soundness of the patient) by measuring serum [Na+]. In addition, the goal weight (at which hydration standing and serum [Na+] focus are normal) might must be recalculated periodically to enable for growth in kids or changes in body fat in adults. Doses ought to be titrated to particular person sufferers because higher doses and more frequent dosing intervals are typically required because of the elevated degradation of the peptide. However, physicians ought to do not overlook that the naturally occurring quantity expansion and reset osmostat that occurs in pregnancy maintains the serum [Na+] at a decrease degree throughout pregnancy. For many others, nevertheless, together with these with the genetic forms, the only practical type of therapy at present is to restrict sodium intake and administer a thiazide diuretic alone236 or together with prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors or amiloride. When mixed with dietary sodium restriction, these drugs cause modest hypovolemia. Monitoring for hypokalemia is recommended, and potassium supplementation is sometimes required. Care must be exercised when treating patients taking lithium with diuretics as a outcome of the induced contraction of plasma quantity may enhance lithium concentrations and worsen potential poisonous effects of the therapy. Indomethacin, tolmetin, and ibuprofen have been used on this setting,249,253,254 though ibuprofen could also be much less effective than the others. However, sufferers with a reset thirst threshold shall be resistant to fluid restriction because of the resulting thirst from stimulation of brain thirst centers at larger plasma osmolalities. Fluid consumption in patients with psychogenic causes of polydipsia is pushed by psychiatric components that have responded variably to behavioral modification and pharmacologic therapy. Several stories have advised restricted efficacy of the antipsychotic drug clozapine as an agent to reduce polydipsia and prevent recurrent hyponatremia in at least a subset of these patients. If a affected person with major polydipsia is troubled by nocturia, this can be reduced or eradicated by administering a small dose of desmopressin at bedtime; as a result of thirst and fluid intake are lowered during sleep, this treatment is much less likely to trigger water intoxication, offered the dose is titrated to enable resumption of a water diuresis as quickly because the affected person awakens the following morning. In contrast, disorders of the renal diluting mechanism often present as hyponatremia and hypoosmolality. Hyponatremia is among the many most common electrolyte disorders encountered in clinical drugs, with an incidence of 0. As reviewed within the introduction to this chapter, Na+ and its associated anions account for nearly the entire osmotic exercise of plasma. Therefore, adjustments in plasma [Na+] are often associated with comparable modifications in plasma osmolality. The osmolality calculated from the concentrations of Na+, urea, and glucose is usually in shut agreement with that obtained from a measurement of osmolality. A lower in the water content material of serum is often due to its displacement by excessive amounts of protein or lipids, which can occur in severe hyperlipidemia or hyperglobulinemia. Normally, 92% to 94% plasma volume is water, with the remaining 6% to 8% being lipids and protein. Thus, when a higher than normal proportion of plasma is accounted for by solids, the focus of Na+ in plasma water remains regular, but the focus in the complete volume, as measured by flame photometry, is artifactually low. Such a discrepancy may be avoided if [Na+] is measured with an ion-selective electrode. Whereas the flame photometer measures the focus of Na+ within the complete plasma volume, the ion-selective electrode measures it solely in the plasma water. Normally, this difference is simply three mEq/L however, within the settings underneath discussion, the difference can be a lot larger. Because the big lipid and protein molecules contribute only minimally to the whole osmolality, the measurement of osmolality by freezing point melancholy stays normal in these patients. Hyponatremia related to regular osmolality has been termed factitious hyponatremia or pseudohyponatremia.
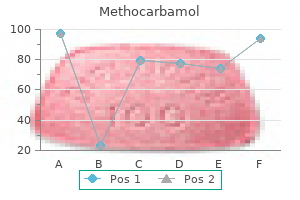
500 mg methocarbamol cheap visa
This appears to be the case muscle relaxant 303 500 mg methocarbamol generic mastercard, though the absolute difference in osmolality between the lumen and peritubular house has been a source of considerable controversy spasms near anus cheap 500 mg methocarbamol visa. These points have been elegantly addressed via characterization of knockout mice with a targeted deletion of aquaporin-1, a water channel protein expressed at the apical and basolateral membranes of the proximal tubule. Mice poor in aquaporin-1 have an 80% reduction in water permeability in perfused S2 segments, with a 50% reduction in transepithelial fluid transport. The physiological relevance of apical Cl-formate and Cl-oxalate exchange has been addressed by perfusing individual proximal tubule segments with options containing Na+-Cl- and formate or oxalate. Both formate and oxalate considerably elevated fluid transport beneath these situations in rabbit, rat, and mouse proximal tubules. Alternatively, apical K+ channels in the proximal tubule could operate to stabilize membrane potential during Na+-Cl- absorption. To protect the electroneutrality of transcellular Na+-Cl- transport, this exit of Na+ throughout the basolateral membrane have to be balanced by an equal exit of Cl-. Increases or decreases in basolateral K+ enhance or lower intracellular Cl-activity, respectively, with reciprocal results of basolateral Cl- on K+ exercise; these knowledge are consistent with coupled K+-Cl- transport. Basolateral anion substitutions have minimal impact on the membrane potential, regardless of appreciable results on intracellular Cl- exercise, nor for that matter do changes in basolateral membrane potential affect intracellular Cl-. Cell swelling thus prompts each K+ and Cl- channels on the basolateral membranes of proximal tubular cells. Dependency of reabsorptive internet fluid flux upon proximal tubular floor area at spontaneous variations of filtration rate. The mathematical analysis of Du and associates provides a superb rationalization of the discrepancy between their results and people of Burg and coworkers. Mathematical analysis of the rabbit knowledge thus predicts a 43% increase in torque because of a 41% improve in tubule diameter at a threefold improve in circulate; this corresponds to the statistically insignificant 36% enhance in volume reabsorption reported by Burg and associates. Fluid shear stress induces densely distributed peripheral actin bands and increases the formation of tight junctions and adherens junctions in cultured tubule cells; this junctional buttressing is hypothesized to maximize flow-activated transcellular salt and water absorption. Peritubular components also play an important additive function in glomerulotubular balance. It has lengthy been appreciated that modifications in peritubular protein focus have essential effects on proximal tubular Na+-Cl- reabsorption; these results are also seen in mixed capillary and tubular perfusion experiments. Androgens improve proximal tubular Na+-Cl- reabsorption via marked induction of renal angiotensinogen, presumptively inside the proximal tubule. These mice also exhibit salt-sensitive hypertension and ultimately a significantly shorter life span in comparability with wild-type mice. The skinny descending limb begins in the outer medulla after an abrupt transition from S3 segments of the proximal tubule, marking the boundary between the outer and inner stripes of the outer medulla. The passive reabsorption of this delivered Na+-Cl- by the thin ascending limb is a important part of the passive equilibration model of the renal countercurrent multiplication system. Consistent with this role, the permeability properties of the thin ascending limb are dramatically totally different from those of the descending thin limb, with a much greater permeability to Na+-Cl- and vanishingly low water permeability. This study thus offered elegant proof for the relative independence of paracellular and transcellular conductances for Na+ and Cl-, respectively, in thin ascending limbs. In collaboration with the countercurrent mechanism, Na+Cl- reabsorption by the thin and thick ascending limbs will increase medullary tonicity, facilitating water absorption by the collecting duct. Claudin-14 interacts with claudin-16, disrupting cation selectivity of the paracellular barrier in cells that also coexpress claudin-19. In explicit, a large variation in single-channel conductance has been reported for basolateral Cl-channels in this nephron section. Phosphorylation of no less than two of these three serines is required for detectable K+ channel activity in Xenopus oocytes; mutation of all three serines to alanine abolishes phosphorylation and transport exercise, and all three serines are required for full channel exercise. The understanding of the cellular group and molecular phenotype of the distal nephron continues to evolve and merits a quick evaluate in this context. Uromodulin is released by proteolytic cleavage at the apical membrane and is secreted as essentially the most plentiful protein in regular human urine (20 to a hundred mg/day). A high-salt food plan will increase uromodulin expression, suggesting a task in ion transport. A, Amiloride-sensitive present in Xenopus oocytes expressing the person subunits and numerous combinationsthereof. Nature 367:463-467, 1994; B from Firsov, D, Schild L, Gautschi I, et al: Cell floor expression of the epithelial Na channel and a mutant inflicting Liddle syndrome: a quantitative strategy. Of broader relevance, these research have served to underline the necessary role for Cl- homeostasis in the maintenance of extracellular quantity and pathogenesis of hypertension. Treatment with these brokers is incessantly associated with fluid retention, suggesting an effect on renal Na+-Cl- transport. Thus, disorders of extracellular K+ have a dominant impact on excitable tissues, mainly heart and muscle. In addition, a growing physique of evidence has implicated hypokalemia and/or reduced dietary K+ within the pathobiology of hypertension, coronary heart failure, and stroke; these and other medical penalties of K+ disorders are reviewed in Chapter 18. Potassium is predominantly an intracellular cation, with only 2% of whole physique K+ residing within the extracellular fluid. Extracellular K+ is maintained inside a very slender vary by three major mechanisms. This part critiques the mechanisms and regulation of transepithelial K+ transport along the nephron. As in different sections of this chapter, the emphasis is on notably recent developments in the molecular physiology of renal K+ transport. These pathways are primarily discussed within the part on renal Na+-Cl- transport; related issues relevant to K+ homeostasis per se shall be particularly addressed in this section. Proximal tubules generate minimal transepithelial K+ gradients, and fractional reabsorption of K+ is just like that of Na+. This absorption is believed to primarily proceed by way of convective transport-solvent drag as a outcome of frictional interactions between water and K+-rather than diffusional transport. However, an increase in interstitial K+ concentration from 5 to 25 mmol/L dramatically inhibits Cl- transport by perfused thick ascending limbs. K+ is secreted into the descending thin limbs by passive diffusion, pushed by the excessive medullary interstitial K+ focus. Descending thin limbs thus have a very excessive K+ permeability, without proof for lively transepithelial K+ transport. Intercalated cells from 4knockouts fail to considerably decrease cell quantity in response to high-K+ diet. A variety of completely different K+ channels have been described in the electrophysiologic characterization of the basolateral membrane of principal cells, which has numerous technical barriers to overcome. However, this seems to be because of marked lack of K+ in the colon rather than within the kidney, as a result of renal K+ excretion is appropriately lowered within the K+-depleted knockout mice. Intracellular magnesium (Mg2+) and polyamines play key roles in inward rectification, binding and blocking the pore of the channel from the cytoplasmic side. Phosphorylation of the N-terminal website overrides the effect of a carboxy-terminal endoplasmic reticulum retention signal, thus increasing expression of the channel protein at the cell membrane. The related mechanisms are mentioned in the context of the difference to K+ loading and hyperkalemia and K+ deprivation and hypokalemia. Histogramsofchannels/ patch are shown for rats on a management food regimen (A), a high-K food plan for six hours(B),andahigh-Kdietfor48hours(C).
Discount 500 mg methocarbamol with visa
Measurements and comparisons ought to be carried out on the identical pulse sequence on serial studies muscle relaxant pharmacology methocarbamol 500 mg cheap. At baseline and on subsequent posttreatment time points spasms right side buy methocarbamol 500 mg mastercard, the longest dimension of extranodal target lesions and quick axis measurement of the node is used for assessing tumor burden and to monitor response. When each cystic and solid metastases are present, stable lesions are preferred as selectable target lesions. Other really nonmeasurable lesions include leptomeningeal illness, ascites, pleural or pericardial effusion, lung lymphangitis, and pores and skin carcinomatosis. Tumor Response Evaluation Measurable illness is defined by the presence of at least one goal (measurable) lesion. At baseline, when more than one goal lesion is current, all lesions up to a most of 5 lesions in whole and a most of two lesions per organ consultant of all concerned organs must be identified as target lesions to report their measurement at baseline and every time level. It is preferable that the goal lesion be clearly defined, be suitable for repeat measurement, and not have been previously treated with local-regional therapy. All other lesions and disease websites, together with pathologic lymph nodes (as described earlier), are designated as nontarget lesions, and only their presence ought to be recorded at baseline. When a goal lesion fragments into multiple smaller lesions, the longest dimension of all fragmented parts are added to the sum. If target lesions coalesce, the longest dimension of the ensuing coalescent lesion ought to be taken. If there are unequivocal lesions, progression ought to be reassessed on follow-up examinations. Moreover, with targeted therapies, morphologic adjustments inside tumors lag behind physiologic and molecular modifications. Tumors handled with focused therapies might not demonstrate change in tumor burden as seen with standard cytotoxic therapies. The common Hounsfield units of the goal lesions is computed before and after therapy. Some of the research have advised utility of Choi standards in response evaluation of early metastatic renal cell carcinoma handled with sunitinib and in gentle tissue sarcoma treated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. There is rising interest in customizing remedy tailored to suit every individual affected person, needing early and correct evaluation of tumor response to therapy. To maintain consistency in imaging, it is recommended to reconstruct 5-mm slices (or less) contiguously. Measurements and comparisons ought to be carried out on the same sequence on serial studies. A periportal lymph node larger than 20 mm in short axis can be considered malignant. Response Assessment Based on Fluorodeoxyglucose�Positron Emission Tomography: Positron Emission Tomography Response Criteria in Solid Tumors the discrepancy between tumor response and decrease in tumor measurement could be very obvious in tumors corresponding to lymphoma and people treated with focused brokers. Therefore, tumor metabolic response as an index of tumor response could be a better predictor of end result than morphologic modifications alone. Response Criteria for Lymphoma Lymphoma is the most typical main hematopoietic malignancy. Unlike metastatic deposits to different organs, lymph nodes are normal anatomic constructions that possess a measurable size. Currently, lymph node size is used to diagnose a lymph node as malignant, as a end result of larger lymph nodes usually tend to be malignant than smaller ones. Similarly, posttreatment scarring at disease sites can continue to show a measurable lesion despite full tumor cell resolution. Lymphoma also can manifest in manners that are challenging to assess objectively on conventional imaging strategies, such as diffuse infiltration of viscera, bone or bone marrow involvement without focal lesion, and total enhance in measurement. Future Trends Advances in imaging applied sciences, distinction supplies, and postprocessing strategies have introduced physiologic and practical assessment to imaging. Newer imaging techniques now possess Key Points � Imaging stays central to monitoring treatment in solid tumor and lymphoid malignancies. Routine availability, reproducibility, standardization, and validation are needed for widespread use. Choi H: Critical issues in response analysis on computed tomography: classes from the gastrointestinal stromal tumor model. This chapter will briefly describe the position of imaging in preprocedural analysis and postprocedural evaluation of abdominal malignancies present process imageguided targeted therapies, with specific focus on hepatic and renal tumors. Image-Guided Treatment Options the past few many years have seen a substantial rise in the performance of image-guided loco-regional therapies for varied tumors within the abdomen and pelvis. Prominent image-guided remedies include percutaneous image-guided ablation and intra-arterial therapies. Whereas percutaneous ablations are most commonly used for 1038 therapy of renal cell most cancers and malignant liver lesions, intraarterial and image-guided radiation therapy are primarily offered in the management of hepatic malignancies. These contain transarterial administration of various particles into vessels supplying the tumor to accomplish tissue destruction. Transarterial embolization techniques are attainable because of the dual hepatic vascular provide (portal vein, 75%; hepatic artery, 25%), which permits selective intraarterial instillation of embolic brokers and chemotherapeutic medication into the tumor because hepatic tumor blood supply is preferentially arterial. The next few paragraphs will discuss several factors requiring careful consideration during assessment before loco-regional therapies. In sufferers with hepatic tumors, the scale and number of lesions dictate the kind of loco-regional therapy with solitary tumors or fewer than three tumors being handled by percutaneous ablation or radiation remedy and a quantity of hepatic lesions are managed with intra-arterial therapies. For percutaneous ablation, tumor measurement has considerable affect on the remedy plan, including willpower of types and number of electrode probes (single vs. In sufferers with oligometastatic liver disease (solitary tumor or <5 tumors measuring three cm), ablative therapies, and image-guided radiation therapy are increasingly offered as an choice to sufferers who refuse surgery or when surgical procedure is contraindicated. For renal tumors, the typical protocol consists of an unenhanced, nephrographic part and delayed phase acquisition. Following initial assessment of therapy response, subsequent imaging follow-up is performed to detect native tumor progression evidenced by recurrence and growth of new local and distant websites of illness. Imaging: Pretreatment Evaluation Imaging is integral to the multidisciplinary care of patients diagnosed with hepatic or renal malignancy as a end result of patient selection is usually carried out depending on the oncologic evaluation, as nicely as the technical feasibility of assorted therapy *References 24, 25, 29, 41, forty three, 44. The tumor dimension additionally dictates the sort of electrode, variety of overlapping ablations, and variety of therapy classes. Precise delineation of tumor location and its relationship to adjacent structures is necessary earlier than percutaneous ablation because it not only determines a safe trajectory to the tumor but in addition influences planning of the process, together with affected person place, sort of electrode, and wish for adjunctive procedures such as hydrodissection. Careful consideration to the relationship of hepatic and renal tumors to structures with the liver and renal hilum is important to avoid inadvertent damage to the biliary tract and renal collecting system or ureter, respectively. Image-guided ablation of tumors close to the hepatic and renal vessels is feasible, and thermal harm to these vessels is proscribed due to blood circulate. Tumors with infiltrative margins are much less more likely to be efficiently handled with percutaneous ablation in contrast with well-encapsulated tumors. A, Contrast-enhanced coronal reformatted computed tomography picture in a 62-year-old man with a big left renal cell carcinoma (thick arrow), with tumor thrombus extending into left renal vein and inferior vena cava (thin arrows). The presence of serious vascular involvement precludes ablative and intra-arterial therapies. Presence of distant metastases adversely impacts end result and is a relative contraindication for loco-regional therapies because these remedy options are usually considered for native tumor management. Preprocedural analysis of regular and variant vascular anatomy must be performed along with identification of preexisting vascular ailments corresponding to arterial atherosclerosis for remedy planning.
Discount methocarbamol 500 mg otc
Neuroblasts from the basal plates may give rise to teams of neurons within the tegmentum of the midbrain (red nuclei muscle relaxant phase 2 block methocarbamol 500 mg order with visa, nuclei of third and fourth cranial nerves spasms thumb joint 500 mg methocarbamol buy otc, and reticular nuclei). The rostral (anterior) a half of the forebrain, together with the primordia of the cerebral hemispheres, is the telencephalon; the caudal (posterior) part of the forebrain is the diencephalon. B, Transverse part of the growing midbrain exhibits the early migration of cells from the basal and alar plates. D and E, Transverse sections of the creating midbrain on the level of the inferior and superior colliculi, respectively. Differential expression of Wnt/-catenin signaling is concerned in the patterning of the hypothalamus. Later, a variety of nuclei involved with endocrine activities and homeostasis develop. Initially, the epithalamic swellings are giant, however later they become relatively small. Proliferation of cells in its walls soon converts it into a solid, cone-shaped gland. The Notch signaling pathway has been implicated within the proliferation and differentiation of pituitary progenitor cells. By the fifth week, the diverticulum has elongated and constricted at its attachment to the oral epithelium. C, Median section of the mind at 7 weeks reveals the medial surface of the forebrain and midbrain. E, Transverse part of the diencephalon shows the epithalamus dorsally, the thalamus laterally, and the hypothalamus ventrally. Cells of the anterior wall of the hypophyseal diverticulum proliferate and give rise to the pars anterior of the pituitary gland (see Table 17-1). The residual cleft is usually not recognizable in the adult pituitary gland; however, it might be represented by a zone of cysts. A, Sagittal section of the cranial end of an embryo at roughly 36 days reveals the hypophyseal diverticulum, an upgrowth from the stomodeum, and the neurohypophyseal diverticulum, a downgrowth from the forebrain. By eight weeks, the diverticulum loses its reference to the oral cavity and is in close contact with the infundibulum and posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) of the pituitary gland. E and F, Sketches of later stages present proliferation of the anterior wall of the hypophyseal diverticulum to kind the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) of the pituitary gland. The infundibulum offers rise to the median eminence, infundibular stem, and pars nervosa. Initially, the walls of the infundibulum are thin, but the distal finish of the infundibulum soon becomes stable as the neuroepithelial cells proliferate. These cells later differentiate into pituicytes, the first cells of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, that are carefully associated to neuroglial cells. It can additionally be recognized in a small number of radiographs of crania of neonates (usually those with cranial defects). Occasionally, a rare, benign tumor (craniopharyngioma) develops in or superior to the sella turcica. As the cerebral hemispheres expand, they cover successively the diencephalon, midbrain, and hindbrain. The hemispheres finally meet each other within the midline, and their medial surfaces become flattened. The mesenchyme trapped within the longitudinal fissure between them provides rise to the cerebral falx (falx cerebri), a median fold of dura mater. The progress and curvature of the cerebral hemispheres have an result on the shape of the lateral ventricles. A large mass (4 cm) occupies an enlarged sella turcica, increasing inferiorly into the sphenoid bone and superiorly into the suprasellar cistern. The inferior half of the mass is stable and appears darkish, whereas the superior half is cystic and appears brighter. The choroid fissure is situated at the junction of the choroid plexus and the medial wall of the lateral ventricle. B, Diagrammatic section of the forebrain reveals how the developing cerebral hemispheres develop from the lateral partitions of the forebrain and broaden in all instructions until they cowl the diencephalon. C, Sketch of the forebrain exhibits how the ependymal roof is finally carried into the temporal lobes because of the C-shaped progress pattern of the cerebral hemispheres (arrows). B, Transverse part of the forebrain at the degree of the interventricular foramina exhibits the corpus striatum and choroid plexuses of the lateral ventricles. C, Similar part at approximately 11 weeks reveals division of the corpus striatum into the caudate and lentiform nuclei by the interior capsule. The creating relationship of the cerebral hemispheres to the diencephalon can be illustrated. As the cerebral cortex differentiates, fibers coursing to and from it pass through the corpus striatum and divide it into caudate and lentiform nuclei. Its pearshaped head and elongated physique lie within the floor of the frontal horn and body of the lateral ventricle, whereas its tail makes a U-shaped turn to acquire the roof of the temporal or inferior horn. This lamina extends from the roof plate of the diencephalon to the optic chiasm (decussation or crossing of the optic nerve fibers). The first commissures to kind are the anterior commissure and hippocampal commissure. The anterior commissure connects the olfactory bulb (rostral extremity of the olfactory tract) and related areas of one hemisphere with these of the alternative side. Cells of the intermediate zone migrate into the marginal zone and give rise to the cortical layers. The grey matter is located peripherally, and axons from its cell our bodies move centrally to type the big quantity of white matter (medullary center). The corpus callosum initially lies in the lamina terminalis, however fibers are added to it because the cortex enlarges, and it steadily extends past the lamina terminalis. The remainder of the lamina terminalis lies between the corpus callosum and the fornix. It turns into stretched to type the septum pellucidum, a skinny plate of brain tissue containing nerve cells and fibers. The walls of the creating cerebral hemispheres initially show three typical zones of the neural tube: Because of the complexity of its embryologic history, abnormal growth of the brain is frequent (approximately 3 of a thousand births). Subnormal mental improvement may outcome from publicity of the embryo or fetus through the 8- to 16-week interval to viruses corresponding to Rubella virus and high levels of radiation (see Table 20-6). Prenatal danger components, corresponding to maternal infection or thyroid dysfunction, Rh factor incompatibility, and a few hereditary and genetic conditions, trigger most instances of cerebral palsy, however the central motor deficit might outcome from occasions throughout delivery. The hernia might contain meninges (meningocele), meninges and part of the mind (meningoencephalocele), or meninges, part of the brain, and a part of the ventricular system (meningohydroencephalocele). The surface of the cerebral hemispheres grows rapidly through the fetal interval, forming many gyri (convolutions), which are separated by many sulci (grooves). Inset at upper right, the smooth lateral (top) and medial (bottom) surfaces of a human fetal mind (14 weeks). C, the lateral (top) and medial (bottom) surfaces of the fetal brain at week 38 (label on picture: forty weeks from last normal menstrual period). A, Sketch of the top of a neonate with a large protrusion from the occipital region of the skull.
Buy methocarbamol 500 mg low cost
External drive applied to erect penile tissue causes a sudden rise in intracorporeal stress spasms medication buy cheap methocarbamol 500 mg online, resulting in additional distention and pressure of the already thinned tunica albuginea back spasms 4 weeks pregnant 500 mg methocarbamol buy visa, thereby inflicting a tear. Intracavernosal hematomas are normally bilateral, resulting from harm to the cavernosal tissue when the base of the penile shaft is crushed against the pelvic bones. Usually, the venous outflow is maintained, preventing complete erection, stasis, and hypoxia. The integrity of the tunica albuginea as properly as the extent and site of a tunical tear may be shown. Associated vascular injuries additionally can be proven by color or power Doppler methods. When a complication similar to an abscess arises, imaging may assist evaluate its anatomic relationship to the corpora and urethra. Multiplanar T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and postcontrast T1-weighted images are acquired. Injuries associated to the adjacent constructions, notably the corpus spongiosum and urethra, are additionally demonstrated. After intravenous administration of gadolinium, enhancement of the plaque has been shown to correlate with the presence of lively inflammation. In the acute phase, cavernosal hematomas seem as hyperechoic or complex masses, which later turn into cystic and often have septations. Cavernosal injury could cause fibrosis, which appears as poorly defined, echogenic scar changing erectile tissue. Real-time examination of the urethra throughout instillation of fluid may show extravasation by way of a ruptured urethral wall. The presence of air in the cavernosal our bodies within the absence of external penetrating trauma is an indirect sign of urethral injury. Ultrasonography might present edema or hematoma of the corpus spongiosum after penile trauma. However, small isolated corpus spongiosal injuries will not be detected by ultrasonography. In instances of thrombosis of the superficial and deep dorsal penile veins, ultrasonography reveals a noncompressible dorsal vein. In sufferers with latest arterial laceration, gray-scale ultrasonography reveals an irregular, but wellcircumscribed, hypoechoic area, secondary to tissue harm or distended lacunar spaces in the corpus cavernosum. In highflow priapism, the arterial-lacunar fistula bypasses the helicine arteries and appears as an aliasing colour blush extending into the cavernosal tissue and as a turbulent high-velocity move on shade duplex ultrasonography. Long-term follow-up imaging with color Doppler ultrasonography is helpful to exclude recurrent fistula and recanalization of the embolized cavernosal artery. The belly reservoir also may be visualized whether it is superficial and is greatest visualized when it has maximum quantity. During routine ultrasonography of the pelvis, the complete stomach reservoir may be Document t�l�charg� de ClinicalKey. Inflating the prosthesis decreases the reservoir volume, confirming the true nature of the fluid. Infection is often a devastating complication of a penile prosthesis and should require antibiotic remedy and prosthetic elimination. Associated inflammation results in corporeal fibrosis and penile shortening, which may make reimplantation troublesome. Ultrasonography can be helpful in figuring out the extent of fibrotic changes, which manifest as focal or diffuse hyperechogenicity of the cavernosa. It also can be utilized to detect patency of the anastomosis and rare complications such as aneurysmal dilatation of the anastomosis. The neourethra manifests as an anechoic tubular structure after the instillation of saline solution into the lumen. A prosthesis in a neophallus may be evaluated on ultrasonography and has the identical look as in a native penis. Radical or whole penectomy with or with out cystoprostatectomy is done for the malignant lesions that contain the proximal shaft or the posterior urethra. Less commonly, surgical repair (ligation of the internal pudendal or cavernosal artery with microsurgical closure of the fistula) or conservative administration with close follow-up is the strategy of management. Phallic reconstruction surgical procedure can be utilized for intercourse reassignment or for correction of congenital penile malformations. Differential Diagnosis Thrombosis of the superficial and deep dorsal penile veins is a uncommon urologic emergency and clinically may mimic penile fracture. Treatment In penile fractures, early surgical intervention can prevent delayed problems corresponding to fibrous plaque formation and angulation of the penis. In Diagnostic imaging of the lower genitourinary tract, New York, 1985, Raven Press. Both conditions predominantly have an effect on young males in the second through fourth a long time of life. Scanning is performed most often with the transducer in direct contact with the pores and skin, however, if necessary, a stand-off pad can be utilized for evaluation of superficial lesions. The measurement and echogenicity of every testis and epididymis are compared with those of the other side. Color Doppler and pulsed-wave Doppler imaging parameters are optimized to display low-flow velocities to reveal blood flow in the testes and surrounding scrotal structures. Power Doppler imaging also could also be used to demonstrate intratesticular flow in sufferers with an acute scrotum. In patients being evaluated for an acute scrotum, the asymptomatic side ought to be scanned initially to set the gray-scale and colour Doppler achieve settings to enable comparison with the affected facet. Transverse photographs with portions of every testis on the same picture must be acquired in gray-scale and color Doppler modes. The constructions throughout the scrotal sac are examined to detect extratesticular lots or different abnormalities. In patients with small palpable nodules, scans ought to embody the world of medical concern. A finger should be placed beneath the nodule and the transducer placed immediately over the nodule for scanning. Alternatively, a finger may be placed on the 940 nodule and the transducer opposite to enable visualization of the lesion. Additional methods such as use of the Valsalva maneuver or upright positioning can be used as wanted for venous evaluation. The penis is dorsiflexed over the pubis and a pad placed over it to retain its place. It is essential to take time with positioning and guarantee affected person comfort, as a end result of any motion both voluntary or from cremasteric contraction could degrade image high quality. The origins of the renal vessels must be included to permit analysis of the lymph node drainage of the testes.