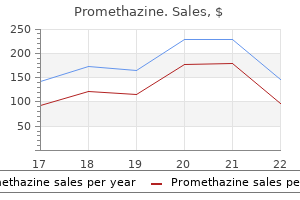
Discount promethazine 25 mg with mastercard
When these two strategies are combined the fixation is labeled as triangular fixation allergy vertigo treatment promethazine 25 mg purchase free shipping. Posterior Span Plating Posterior span plate acts as a buttress plate extending from one iliac wing to another allergy medicine breastfeeding discount 25 mg promethazine fast delivery, lying within the subcutaneous plane. Sharply elevate the glutei attachment from the iliac crest and outer table of the ilium. Biomechanical comparison of posterior inner fixation techniques for unstable pelvic fractures. Vertically unstable pelvic fractures fixed with percutaneous iliosacral screws: does posterior injury sample predict fixation failure. Technical elements and really helpful treatment algorithms in triangular osteosynthesis and spinopelvic fixation for vertical shear transforaminal sacral fractures. Because of increasing street side accident, the burden of the disease can be increasing. Usually acetabulum fractures occur primarily in young adults due to excessive velocity trauma. There is big accountability on the orthopedic surgeons to provide a satisfactory consequence in these tough fractures, so that the young trauma victims can stay a standard productive life. Until the center of twentieth century, majority of acetabular fractures were handled nonoperatively. In 1950s and Nineteen Sixties, few studies reported equivocal end result of both operative and nonoperative administration in these fractures. There was a revolutionary change within the management of those tough fractures when Judet brothers and Leuternel in 1964 reported that the result of operative therapy of acetabulum fractures were much better than nonoperative treatment. They proposed a classification system primarily based on radiology and really helpful treatment accordingly. Despite these advancements, the basic ideas proposed by Leuternel and Judet and by Matta remains the same. Hence, anatomic reduction of the articular surface with steady fixation is essential for successful consequence. Acetabulum is actually fashioned at the junction of the ilium, ischium, and pubis after fusion of the triradiate cartilage. The anterior column includes 1464 TexTbook of orThopedics and Trauma the path of drive transmitted by way of head of femur to the acetabulum often decides the pattern of injury. A lateral direct pressure over the larger trochanter often causes medial wall of acetabulum fracture (quadrilateral fracture) or central fracture dislocation. If the hip is flexed 90� and the force is along the axis of femur with femur in neutral or delicate abduction, it might break the posterior wall of acetabulum. In adduction of femur, the hip joint may fully dislocate with none fracture of acetabulum. These two columns are connected to the sacroiliac articulation by a thick strut of bone mendacity above the higher sciatic notch called sciatic buttress. The roof of the acetabulum is the thick, weight-bearing portion, and types a separate fragment in each column fractures. The thin quadrilateral plate forms the medial wall or the floor of the acetabulum. Both the quadrilateral surface and the iliopectineal eminence are skinny and adjoining to the femoral head, limiting the types of fixations that can be utilized in these regions. History and Physical Examination Acetabulum fractures are usually related to other system injury. A thorough initial examination is crucial to establish lifethreatening situations and other associated harm (seen in about 50% of the patients). The fundamental principles of trauma management and resuscitation apply to the acetabular fractures. Distal femur fracture or femoral shaft fractures may be present that would have an result on the administration of the acetabular fracture. Local examination of the hip, pelvis and the extremity additionally bears an necessary implication in deciding the sort of injury and subsequent management. The subcutaneous tissue is detached from the underlying fascia and thus, create a cavity, which locations this tissue in danger for an infection and/or poor healing. Abductionandadductionofthehip: To detect instability, push the hip downward on 90� hip-flexed posture. Limb-lengthdiscrepancy: It may present hint for the presence of incarcerated intra-articular fragments and hip dislocation. In isolated posterior dislocations or with associated acetabular fractures, sciatic nerve may be damaged. Preoperative documentation of perform this nerve is necessary as a result of iatrogenic harm of this nerve can also be widespread in posterior strategy to acetabulum. Theroofofacetabulum: the roof represents the best point and the weight-bearing portion of the acetabulum. In a accurately taken obturator indirect view, the anterior and posterior iliac spines are superimposed, the iliac wing is slim and correspondingly, the obturator foramen is seen as giant as potential. Disruption of any of the traditional lines of the acetabulum represents a fracture involving that portion of the bone. Displacement of the articular floor is interpreted by displacement of those normal strains of the acetabulum. Iliopectineal line: the iliopectineal line or iliopubic line is the radiographic landmark for the anterior column. It begins at the sciatic notch and travels along the superior pubic ramus to the symphysis pubis. It begins on the sciatic notch, coursing inferiorly to the medial boarder of the ischium. In a accurately taken iliac oblique view, the iliac wing is seen broadly unfold out and the obturator ring is as thin as attainable. In most cases, the fracture may be categorized properly from plain radiographs alone. Plain radiographic views are often best for assessing the congruence between the femoral head and the roof of the acetabulum. Another major parameter that could be evaluated from radiographs and which has major implication in deciding nonoperative or operative intervention in acteabular fracture is "roof-arc angle". Roof-arc Angles13,14 these are used to assess the scale of the intact portion of acetabulum dome. Another line is drawn by way of the purpose the place the fracture line intersects the radiographic roof of the acetabulum and again to the geometric heart of the acetabulum. The roof-arc measurements roughly describe the place and orientation of the acetabular fracture and, due to this fact, the intact portion of superior acetabular articular floor. For consideration of nonoperative remedy, the pinnacle should stay congruous with the roof of the acetabulum on the three views. The interpretation of roof-arc measurement for decision of surgical procedure is read as: without traction, all roof-arc measurements ought to be greater than 45� for consideration of nonoperative treatment.
Promethazine 25 mg purchase amex
The transverse carpal ligament could be located at the base of the hand allergy medicine while pregnant promethazine 25 mg low cost, with its proximal boundary being at the distal wrist crease and its distal boundary along the cardinal line allergy medicine for cats promethazine 25 mg buy cheap. The cardinal line courses from the hook of the hamate to the ulnar base of the thumb. The data of these floor landmarks might help in plenty of surgical procedures on the hand. Note that the wire at palmar digital crease is situated over middle of the proximal phalanx (arrow 1). This perform is achieved by a bony skeleton of many small bones and its association with the fibrous skeleton. The skeleton of the hand is split into five rays, each ray making up a polyarticulated chain of the metacarpals and phalanges. The first ray continues with the exterior column of carpus formed by the scaphoid and trapezium. The first metacarpal makes an angle of 45� with the second metacarpal/ plane of palm of the thumb in the sagittal airplane creating a spot between the thumb ray and palm. The ulnar three digits flex obliquely whereas the index finger flexes in the sagittal aircraft. The flexor tendons and the neurovascular bundles emerge through the intervals between the slips. Fibrous flexor sheath types osteofascial tunnel containing the long flexor tendon enclosed within the digital synovial sheath. Midpalmar Space It is a triangular house extending from distal margin of the flexor retinaculum to the distal palmar crease. Its anterior boundary is fashioned by flexor tendons of third, 4th and fifth fingers, 2�4th lumbricals and palmar aponeurosis. It is bound medially by medial palmar septum and laterally by intermediate palmar septum. Thenar Space It is a triangular house extending from the distal margin of the flexor retinaculum to proximal transverse palmar crease. It is certain anteriorly by brief muscle tissue of thumb, flexor tendon of index finger, 1st lumbrical and palmar aponeurosis. It is sure posteriorly by the transverse head of adductor pollicis and medially by intermediate palmar septum. Fibrous Skeleton Superficial palmar fascia extends between the flexor retinaculum, which types its proximal boundary, and the root of the fingers, forming its distal limit. Deep fascia of hand types the flexor retinaculum, palmar aponeurosis and fibrous flexor sheaths. Flexor retinaculum is a fibrous band, which bridges the anterior concavity of the carpals and converts it right into a tunnel (flexor carpal tunnel). Compression of the median nerve in the flexor carpal tunnel leads to carpal tunnel syndrome. It covers the superficial palmer arch, long flexor tendons, terminal part of median nerve and superficial branch of the ulnar nerve. It is triangular in shape and divides into four slips reverse the metacarpal heads of medial four fingers. Each Hypothenar Space It extends from ulnar palm to 5th metacarpal and is localized to hypothenar muscular tissues and its fascia. Flexor Zones of the Hand the hand has been divided arbitrarily into 5 flexor zones. Zone 3 lies between the distal palmar crease and the distal fringe of transverse carpal ligament. The cruciform pulleys are thin and are located between the A2 and A3 pulleys (Cl), between the A3 and A4 (C2) and between the A4 and A5 pulleys (C3). The primary function of these pulleys is to maintain the tendon aligned throughout flexion and in addition to forestall bowstringing of tendons. This extensor retinaculum has six compartments via which the extensor tendons pass. These compartments stop bowstringing of the extensor tendons and supply reliable landmark for surgical approaches. Tenosynovitis can be widespread on this area and is named intersection syndrome. The fourth compartment 1718 TexTbook of orThopedics and Trauma contains the tendons of extensor digitorum communis and extensor indicis proprius. Tenosynovitis and spontaneous rupture of the tendons of this compartment due to rheumatoid arthritis is commonly seen. Attritional rupture happens because of dorsally displaced ulnar head or because of synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. Radiocarpal Joint this joint is formed between the distal articular surfaces of radius and scaphoid, lunate and triquetral bones. The proximal articular floor has a shallow melancholy, whereas the distal articular floor has a protrusion. It is a synovial joint, spherical in shape strengthened by the radial and ulnar collateral ligaments on either facet of the joint. Palmar and dorsal radiocarpal ligaments cowl the front and back of the wrist joint. The anterior interosseous nerve and a deep department of the radial nerve innervate it. The primary movements of the wrist joint are flexion, extension, abduction and adduction. The wrist can be moved in circumduction when a mix of these actions is used. The 2nd metacarpal articulates with three carpal bones specifically trapezium, trapezoid and capitate, while 2nd, third and 4th metacarpals articulate with the capitate. The capsules of these joints are pliable in the entrance and back and rigid on the perimeters. Metacarpal head is slender dorsally and due to the projection of the condyle anteriorly, the collateral ligaments are tight in flexion and relaxed in extension. They are also supported by the accent ligament whose origin is just like that of the collateral ligaments, but they insert into the volar plate. Interphalangeal Joints these are positioned between the phalanges and are synovial hinge joints. Strong fibrocartilaginous plates, which exchange the Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand the intrinsic muscle tissue are positioned within the palmar aspect of the hand and occupy the house between the metacarpals. Arterial Arches of Hand the arterial supply to hand comes from the radial and ulnar arteries. The palmar arch is accomplished by one of many branches of radial artery (superficial palmar branch, radialis indicis and princeps pollicis) on the lateral aspect. Deep Palmar Arch It is shaped by the direct continuation of radial artery beyond the gap between the two heads of the adductor pollicis. It is completed at the base of the fifth metacarpal by the deep branch of ulnar artery. The lymph of the thumb and index finger together with lateral half of volar floor of the hand drains into axillary group of lymph nodes alongside the cephalic vein.
Discount 25 mg promethazine fast delivery
Articulated external fixator has been used as an different selection to allergy treatment 4th cheap 25 mg promethazine with amex transfixation in cases of advanced elbow trauma allergy medicine for 2 year old discount promethazine 25 mg overnight delivery. Wherever attainable, the vessels could also be repaired or a venous graft could additionally be used to obtain revascularization. Debridement of the Wound the wound is thoroughly debrided and prophylactic antibiotics administered. In all instances of excessive vitality trauma the wound ought to ideally be debrided inside 6 hours of the traumatic occasion. A thorough lavage helps to take away the contaminants and thereby minimizes the risk of infection. In the absence of infection, delayed closure of the wound may be carried out after about one week which can be aided by split or full thickness pores and skin grafts relying on the need for coverage. Early wound coverage with skin grafts and flaps is most popular so as to decrease infection, tissue edema and tissue dying and allow early mobilization. Stabilization of Skeletal Injuries Since this injury has multiple fractures and dislocations, an try to correct all displacements at one go may lead to correcting none. Internal fixation is the popular stabilization modality in closed fractures and in clean open grade one and grade two injuries. Comparison of the outcomes of a staged protocol utilizing preliminary joint spanning external fixation and delayed definitive fixation to acute definitive fixation in open distal humerus fractures proved the effectiveness of the previous. When indicated, amputation is usually done on the stage of the fracture website in the humerus. According to earlier reports,9 amputation used to be indicated in virtually 50% of the circumstances. However, today, the appearance of microvascular surgical procedure, revascularization and numerous pores and skin flaps has changed the situation, and amputation could additionally be required less generally. Also bone grafting procedures, reconstruction of the extensor mechanism and free fibular transfers could also be required at a later date. Prosthetic Replacement In case of in depth and irreplaceable articular bone loss, custom-made or modular endoprosthesis can be used to obtain a great useful end result. However, a good musculature within the arm and forearm together with a viable pores and skin cowl is mandatory to carry out this procedure. Rehabilitation in the acute stage is aimed toward prevention of deformity and to hold joints supple for secondary procedures. Open fractures and the incidence of infection within the surgical debridement 6 hours after trauma. Spontaneous defect remodeling in a distal humerus fracture with intensive osseous loss: a case report of a complex elbow fracture. Otem iam ocaveroxim iam omnirit, Catus, quam quius pubissi liquones pon halis incuppl. Opio vit atilis, se efacrit, que quast pulegereo tussum, quistam ium mentere vilicae caet advert crehemp lintem, Patus Puliistatus bonficon tanteris, quam diemus; erum potem tereculibus me consuli nimaximis nos, cone commovi diurnu sentrat iuropte renatam iam ad re publibunu se prorimiu mentius; norionf icepos in publis, ortamquam se tatquit iemqua omne cons sil tem perteliem. Ossed is extra, perum re quissid iaet remquos tilissenium nosterion vivivid ienatum a nocre ac tem publinatus elum anum conos cerit. The term Monteggia fracture is known as after Giovanni Batista Monteggia, who first described this injury in 1814. Monteggia Equivalents TypeIequivalents: � Isolated radial head dislocation: Pulled elbow, Nursemaids elbow � Isolated radial neck fracture � Diaphyseal ulnar fracture with radial neck fracture � Diaphyseal ulnar fracture with fracture of proximal third radius � Diaphyseal ulnar and olecranon fracture with anterior dislocation of radial head � Diaphyseal ulnar and posterior dislocation of the elbow � fracture of proximal one-third of radius. Annular ligament: Surrounds the radial neck and maintains the position of radial head throughout the notch. If this ligament buckles underneath the dislocated radial head, its discount turns into difficult. Interosseousligament: Consists of oblique fibers running from radius proximally to ulna distally. Bonyanatomy: Radial head is elliptical in shape which contributes to the tightness of ligaments because it rotates. Radial shaft has a bow laterally which tightens the oblique and interosseous ligament in supination. Muscle and nerves: Biceps muscle is a flexor of the elbow and supinator of forearm. The pull exerted by biceps is the primary factor liable for radial head dislocation in extended position of elbow. Diagnosis Clinically, a Monteggia fracture reveals itself by pain, useful incapacity of the elbow and a characteristic deformity. Radiography: A radiograph of the forearm that including elbow and wrist is crucial to make a diagnosis. In the lateral view, a line drawn from the middle of the radial head ought to move through the center of the capitellum regardless of the diploma of flexion or extension of elbow. A strict lateral view is essential; else the dislocation of the radial head could additionally be missed. Monteggia fracture dislocation could be confused with congenital dislocation of the radial head. Closedreduction: this should be accomplished underneath common anesthesia or a minimum of beneath sedation, and fluoroscopic management. Longitudinal traction is given to keep the length of ulna, combined with an aligning stress at the apex of the deformity. Once the size and alignment of ulna is maintained, the radial head reduces spontaneously upon flexing the elbow to 90� or extra. Elbow must be maintained in 100�120� flexion to alleviate the dislocating force of biceps muscle. Operativemanagement: Inability to cut back or keep reduction of ulnar fracture or radial head dislocation by closed technique is an indication for operative management. Kocherapproach: Internervous aircraft is between anconeus and extensor carpi ulnaris. This provides excellent visualization of radio capitellar joint and ulnar fracture can be approached via the same incision. When a longitudinal pressure is utilized over forearm, this ends in an elbow dislocation. If the ulna fails to maintain the drive applied, it ends in fracture of proximal ulna with posterior dislocation of radial head. Ulnar fracture is decreased by traction and radial head is reduced by a posterior to anterior directed force. This entails longitudinal traction to align the ulna with a valgus force exerted on the elbow. Immobiliztion is done with elbow in varying degrees of flexion relying upon the place of reduction as confirmed by fluoroscopy.
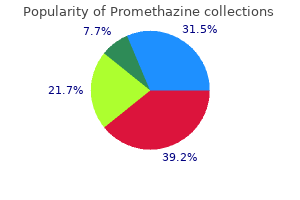
| Comparative prices of Promethazine |
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Menard | 248 |
| 2 | Best Buy | 903 |
| 3 | Barnes & Noble | 106 |
| 4 | GameStop | 295 |
| 5 | Subway | 161 |
| 6 | Darden Restaurants | 911 |
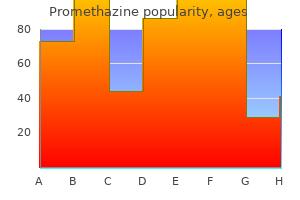
25 mg promethazine effective
Next mould allergy treatment uk promethazine 25 mg mastercard, the psoas with the femoral nerve is retracted as a unit after inserting a rubber catheter round them allergy medicine stronger than allegra promethazine 25 mg discount visa. After dissecting the iliac vessels with the associated lymphatic tissues as a single unit, together with the areolar tissue round them (to shield the lymphatics and prevent postoperative swelling of the limb), these tissues are held along with a third rubber catheter. The periosteum on the inner surface of the pelvis along the quadrilateral plate is now cleared. The exposure is now established via three home windows, as follows: (1) Retracting the psoas medially permits publicity of the internal iliac fossa, (2) the pelvic brim, and (3) the anterior sacroiliac joint. This exposure is facilitated by flexing and internally rotating the hip to loosen up the iliopsoas. The middle window is created by retracting the psoas laterally and the vessels medially. This allows the superior pubic ramus and the quadrilateral plate to be visualized. The medial window is seen by retracting the vessels laterally and the spermatic wire medially. This maneuver offers entry to the remainder of the pubic ramus, the pubic symphysis, and the quadrilateral surface. The most medial part can best be visualized with lateral retraction of the spermatic wire. The periosteum is sharply raised from the iliac crest, and the iliopsoas is stripped from the interior of the ilium. The interval between the sartorius and the tensor fascia lata is developed to expose the rectus femoris if exposure of the hip joint is required. The publicity could be extended along the lateral aspect of the ilium by stripping the gluteal muscle tissue to fracTures of aceTabulum see the anterior facet of the hip joint and anterior inferior iliac backbone. To get broad publicity, direct head of the rectus femoris, which is part of the hip joint capsule, can additionally be incised. No dissection of the femoral vessels, as within the ilioinguinal method, is required. Another drawback is that medial to the iliopectineal eminence, the exposure must be established with the ilioinguinal strategy, which normally limits fixation options to screws or quick plates in this method. Also, injury to the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is difficult to forestall with this method. Often, due to the excessive velocity of the injury, comminution is intensive, and piecing all of the fracture fragments collectively is similar to solving a jigsaw puzzle. Analysis of the fracture pattern, displacement of the fragments, and meticulous preoperative planning go a good distance in easing the difficulties faced in the surgical remedy of acetabular fracture. Of these at least one assistant should have some data and experience in treating acetabular fracture. King Tong, Queen Tong and Farabeuf clamps can be extremely helpful to obtain discount. For using the Farabeuf clamp two screws need to be passed adjoining to the fracture website. This technique must be used with caution; so as to keep away from damage to neurovascular construction. The articular floor is reconstructed to the mildew of the peripherally reconstructed innominate bone. Provisionalfixation: Provisional fixation normally is established via Kirschner wires (K-wires) and, typically, cerclage wires. Definitive fixation: Definitive fixation is established with the next: � Screws: the first fixation often is by means of an interfragmentary screw. The actual nature and placement requires careful preoperative planning and is dependent upon the fracture pattern. It is skinny and simply contoured in both planes, so it can be utilized perfectly to the pelvis. The curved plates are slightly thicker and have a sloping undercut screw hole, permitting extra oblique placement of the screw by way of the plate. In this situation, a plate placed buttressing the medial wall can management the medial migration. This is often a reconstruction or a small fragment T-plate with a pointy right-angled bend going over the pelvic brim down to the quadrilateral surface. It is overcontoured to perform nearly like a spring and maintain the comminuted medial wall. Cerclagewires27: the usage of cerclage wires through the larger sciatic notch or, sometimes, the lesser sciatic notch, around and over the anterior side of the pelvis on the stage of the anterior inferior iliac spine is a really effective method for provisional fixation in certain fracture patterns. This technique is useful in some difficult-to-hold posterior column fractures, transverse, T-shaped, and both-column fractures by which the posterior fracture line exits high in the sciatic notch, offering a beak for the cerclage wire to maintain. The use of cerclage wires, however, does entail slightly extra dissection of the outer table when using the ilioinguinal method or an extensile method (not often used). Reduction and Stabilization of Common Fracture Patterns Reduction and stabilization of a variety of the frequent fracture patterns are mentioned beneath: Posterior wall or lip fracture: Exposed by way of the KocherLangenbeck strategy, the fracture hematoma is washed out and the fracture site cleaned. This needs to be derotated and elevated and the metaphyseal defect filled with cancellous bone graft (usually from the greater trochanter) earlier than dealing with the wall fragment. A subchondral screw often is used to help the reconstructed articular surface. In a extremely comminuted posterior wall fracture, it is most likely not attainable to lag every individual fragment fracTures of aceTabulum 1475 posterior-to-anterior lag screw is then inserted across the obliquity of the transverse fracture line into the anterior column. The starting point of this screw is approximately three fingerbreadths above the acetabulum and requires a big retraction of the abductor musculature. This screw begins proximal to the skinny a part of the quadrilateral plate and runs parallel to the plate, taking purchase within the anterior column. Its position within the anterior column is checked utilizing the obturator indirect view and its extra-articular placement confirmed on the iliac oblique view intraoperatively. It is important to avoid excessive anterior penetration with the drill bit in order to prevent harm to the femoral vessels, which are caught down there by the iliopectineal fascia. When one makes use of the posterior method, the reduction of the posterior column is carried out. Indirect reduction of the anterior column is then attempted through the use of a bone hook to pull the displaced anterior column into the acute angle created by the intact anterior column and the reconstructed posterior column. The bone hook or a pusher on the quadrilateral plate controls the rotation of the anterior column. Reduction is confirmed by palpation of the quadrilateral plate, and the anterior column is stabilized to the reconstructed posterior column utilizing posterior-to-anterior lag screws. A finger is positioned on the quadrilateral surface, and the hip is taken through a variety of motion to rule out intra-articular hardware penetration. When utilizing the anterior approach, the anterior column is reduced first, and oblique discount of the posterior column is tried via the quadrilateral plate by using a small bone hook or a cerclage wire, after establishing lateral traction using a Schanz screw in the femoral head.
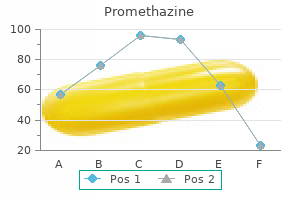
Promethazine 25 mg generic
They usually are misdiagnosed as inflammatory synovitis and handled with anti-inflammatory medication and local steroids allergy treatment elderly discount promethazine 25 mg on line, which can aggravate the signs allergy symptoms fever buy promethazine 25 mg without prescription. When these infections are suspected, it is important to take a biopsy Fungal Infections Three types of manifestations are noticed with fungal infections involving the hand. The most typical are the cutaneous infections, the subcutaneous and deep infections being the opposite. They infecTions within the hand Table 6: Common medicine helpful in mycobacterial infections Atypical mycobacteria Chemotherapy used based mostly on tradition sensitivity M. The subcutaneous an infection includes sporotrichosis, which is often seen horticulture staff presenting with post-traumatic nodule, which progresses alongside the lymphatics. It is treated medically with "itraconazole" Chronic paronychia is one other infection, which has. They require systemic antifungal medicines like "amphotericin B" with radical surgical debridement and even amputation. Study of Antibiotic Resistance Pattern in Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with Special Reference to Newer Antibiotic. Cosgrove Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the Treatment of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Adults and Children. Acute paronychia: comparative therapy with topical antibiotic alone or together with corticosteroid. Closed-catheter irrigation is as efficient as open drainage for therapy of pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis. Necrotizing fasciitis: scientific presentation, microbiology, and determinants of mortality. Tuberculosis amongst European sufferers with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. The usual trigger is a compartment syndrome of the forearm or traumatic interruption of arterial blood circulate, leading to ischemia of the forearm muscles, primarily flexors. Often the surgeon has to be satisfied with just a fractional return of perform or the mere correction of the deformity. Free vascularized muscle grafts, first accomplished in Shanghai, China in 1976, have been reported to be displaying "extremely good" outcomes (Tsuge, 1994). But, may this refined and specialised therapy be accessible, if and when potential, to our Indian patients. Most of them are victims of this dysfunction as a result of the nonavailability of fundamental medical services in most rural and remote villages of India, as properly the normal religion of our individuals in "bonesetters" Tight bandaging by these bonesetters (rather. These philosophical words by Sir Jones could also be true for India at present, however the alarmingly high variety of cases still reported by Indian staff may only be the tip of the iceberg. Richard von Volkmann from Halle described the condition in 1869 and later in 1875 as "a deformity of the hand and wrist resulting from an interference of some nature with the blood provide of the muscle tissue of the forearm. This condition was often preceded by the appliance of tight splints or bandages for the fracture of the humerus in the region of the elbow joint" Again, in his classical. He pointed out that the contracture comes on typically after the initial paralysis. The brachial artery may be lacerated, contused or angulated across the fracture edge in supracondylar fractures of the humerus. Immediately beyond this website, the artery and median nerve move beneath the fibrous arch shaped by the vertical insertion of the biceps tendon and its horizontal enlargement, the lacertus fibrosus fascia. Immediately beyond the lacertus fibrosus fascia, the brachial artery divides into the more superficial radial artery and the deeper ulnar artery. This artery with its main department, the interosseous artery arises from the ulnar artery and posterior interosseous arteries. The anterior interosseous artery passes distally on the interosseous membrane and is the solely real blood provide to the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus. Eaton and Green (1972)8 defined how the median nerve is also anatomically vulnerable to compression. It accompanies the brachial artery beneath the biceps-lacertus fibrosus arch and then enters the substance of the pronator teres, normally passing between its superficial (humeral) and the deep (ulnar) heads. As it emerges, it passes beneath a thickened band of fascia that connects the humeral and ulnar origins of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle. The median nerve could be very generally compressed at this point, diffusely by the swollen, contracted or fibrotic pronator teres muscle and domestically by the sharp unyielding edge of the conjoined origin of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle. Instead, they be part of the brachial or radial arteries proximal to the pronator teres. A single exception is the posterior interosseous branch anastomosing with the lateral elbow collateral vessels. The posterior interosseous artery, nevertheless, lies in the dorsal compartment and might shunt blood to the volar compartment solely when the common interosseous artery is patent, and the strain gradient is enough to produce flow toward this compartment. Eaton and Green (1972) described a traumatic ischemia edema cycle, which ends up in compartment syndrome. At an early level in this process, strain receptors throughout the muscle itself set off a proximal reflex vasospasm affecting all vessels in this common area. Mubarak and Carroll (1979) 6 said that these complicated signs are brought on by circulatory disturbances of muscle tissue and nerves in closed osteofascial compartments due to build-up of tissue fluid stress inside the compartment. However, the classic location is within the volar or flexor compartment of the forearm. This compartment has several unique features that emphasize the anatomic components involved within the contracture, it has a strong facial roof, and at its entrance lay two potential obstructions. The second is the cumbersome pronator teres muscle, which arises from the medial epicondyle and passes obliquely beneath the inelastic lacertus fibrosus to create a V-shaped sphincter beneath which the brachial artery and median nerve must move to enter the flexor compartment. Edema, hematoma or intramuscular hemorrhage on this essential area may trigger sufficient compression of these neurovascular buildings to precipitate the ischemia-edema cycle. There is an anatomic reason why this entity is so typical in the flexor side of the forearm, although extra casts are applied elsewhere over the body. In the unreduced supracondylar fracture of the humerus, the forearm is displaced backward, the fold of deep fascia kinking the brachial artery and the veins around the lower end of the humerus. Also because of backward displacement and the swelling concerning the flexed elbow, the pores and skin is drawn tight across the antecubital area, compressing off the main venous return of the forearm, which is subcutaneous and anterior. Morbid Anatomy1 Volkmann (1981)1 in his third paper confirmed the modifications within the muscle to be necrotic. This concept can be nicely understood when making an allowance for that the cause of this entity is the compartment syndrome complicated. Circulation in the course of the muscle stomach is the most severely impaired, whereas collateral circulation is healthier retained towards the edges of the muscle. The muscles most severely affected are the flexor digitorum profundus and the flexor pollicis longus with less involvement towards the proximal and distal surfaces. The muscle assumes an elongated ellipse form in the path of the long axis, centered across the anterior interosseous artery. Therefore, the muscles most severely affected are the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus, followed by flexor digitorum superficialis and pronator teres, whereas degeneration of wrist flexors and extensors and brachioradialis is comparatively mild.
25 mg promethazine proven
One potential drawback of each acellular nerve grafts and synthetic conduits is the shortage of Schwann cells to promote the directional outgrowth of axons to bridge a defect allergy symptoms rash on face promethazine 25 mg lowest price. More recently allergy symptoms gas purchase 25 mg promethazine fast delivery, stem cells have been launched to improve tissueengineered nerve grafts. In an experimental study of huge radial nerve defects in rhesus monkeys, acellular nerve allografts incubated with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells led to a similar recovery of nerve function compared with autogenous nerve grafts and Schwann cell-laden allografts. Further potential future instructions in this field as proposed in a current literature evaluate comprise the utilization of growth components to improve axon progress and chemotaxis. Effectiveness and safety of stem cell-enhanced tissue-engineered nerve grafts in people, nonetheless, is but to be established and should be in contrast with autologous nerve grafts as the current gold commonplace. Vascularized Composite Tissue Allotransplantation Since the profitable first hand transplantation in 1998, the sphere of vascularized composite tissue allotransplantation in the upper extremity has quickly expanded. The mixture of allotransplantation with synthetic tissue regeneration will help reconstruct what was beforehand irreplaceable. The surgeon and clinical judgment, nonetheless, will continue to play the pivotal role in care of the patient. Three-dimensional engineered bone-ligament-bone constructs for anterior cruciate ligament alternative. In vitro and in vivo analysis of orthopedic interface restore using a tissue scaffold with a steady exhausting tissue-soft tissue transition. In vitro pre-vascularisation of tissue-engineered constructs: a co-culture perspective. One-stage human acellular nerve allograft reconstruction for digital nerve defects. Functional consequence following nerve restore in the upper extremity using processed nerve allograft. Trends within the design of nerve steerage channels in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. Peripheral nerve repair in rats using composite hydrogel-filled aligned nanofiber conduits with incorporated nerve growth factor. Peripheral nerve regeneration through hydrogel enriched chitosan conduits containing engineered Schwann cells for drug supply. Recellularized nerve allografts with differentiated mesenchymal stem cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration. Repairing massive radial nerve defects by acellular nerve allografts seeded with autologous bone marrow stromal cells in a monkey model. Upper extremity transplantation: present concepts and challenges in an rising area. Supplementation of acellular nerve grafts with pores and skin derived precursor cells promotes peripheral nerve regeneration. Composite tissue allotransplantation and dysregulation in tissue restore and regeneration: a job for mesenchymal stem cells. Upperextremity transplantation utilizing a cell-based protocol to minimize immunosuppression. Adipose- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells prolong graft survival in vascularized composite allotransplantation. Vascularized composite allotransplantation: present requirements and novel approaches to stop acute rejection and chronic allograft deterioration. Section 24 � � Injuries of Wrist Section Editor: Prakash P Kotwal � � Surgical Anatomy of the Wrist Prakash P Kotwal, Samarth Mittal, Bhavuk Garg Fracture of the Distal End Radius Prakash P Kotwal, Vivek Shankar Examination of the Wrist Sureshwar Pandey Distal Radioulnar Joint Binu P Thomas, R Sreekanth 219 Chapter Surgical Anatomy of the Wrist Prakash P Kotwal, Samarth Mittal, Bhavuk Garg Introduction the forearm and hand are linked to one another by the wrist. Thus, the wrist helps in transfer of all motions and forces of the hand to forearm. General Anatomy the proximal carpal row consists of, from radial to ulnar side, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum and pisiform whereas trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and hamate kind the distal row in the same order. It may be pertinent to mention right here that the pisiform, which is actually a sesamoid bone within the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris, is taken into account to be a half of the proximal carpal row because it helps in its stabilization through the pisotriquetral joint. The orientation and position of the carpus change repeatedly to be able to make this possible and also to keep joint congruency. The bones of the distal carpal row usually move as a unit by forming a transverse rigid arch and support the 5 metacarpals. The wrist is a posh hinge joint having the first transfer ments of flexion and extension, and secondary movements of radial and ulnar deviation brought about through an oblique screw axis situated inside the head of capitate. On a mean, motion on the wrist ranges from 80� of flexion to 60� of extension, 20� of radial deviation to around 40� of ulnar deviation. In addition to their very own movement in radial and ulnar direction, scaphoid and lunate also flex and lengthen during ulnar and radial deviation of the wrist. Articular floor of distal radius is angled in each planes (around 11� in sagittal aircraft and round 24� of ulnar inclination in frontal plane) and can be biconcave. Scaphoid fossa has a triangular or oval shape with a larger curvature than lunate fossa which is shallower and rectangular. The carpals kind an arc with concavity on the palmar facet closed by the transverse carpal ligament. This ligament types the roof of carpal tunnel which is a standard web site of median nerve compression in the wrist. Moreover, variations of their shape and size are frequent and make them much more tough to understand. However, they are often appreciated well intraarticularly particularly by way of an arthroscope. Ligaments that each take origin and insert into the carpus are intrinsic ones whereas the ones that attach outdoors the carpus are extrinsic ligaments. Both of them differ from each other anatomically, histologically and biochemically (Table 1). Applied: Space of Poirier (frequent site of perilunate dislocations as a end result of its relative weakness) is shaped by its medial prolongation. These deep extrinsic ligaments follow a vertical course and get attached to the lunate and triquetrum, respectively on the anterior aspect. Intrinsic Carpal Ligaments Intrinsic carpal ligaments consist of fibers which both join the proximal and distal carpal bones transversely or connect the two rows collectively. The proximal fibrocartilaginous membrane separates the micarpal from radiocarpal area. Applied: There is absence of any midcarpal ligament between the capitates and lunate. Since wrist has no collateral ligaments so medially carpi ulnaris tendon and laterally abductor pollicis longus tendon substitute for his or her operate. There are six fibroosseous compartments lodging the next tendons (from dorsolateral to dorsomedial direction). Proximally, the sheaths prolong to a variable extent and distally they end beyond the retinacular extension. In the 4th compartment, deep to the tendons, the posterior interosseous nerve ends as a pseudoganglion and the anterior interosseous artery ends anastomosing the fine native articular arteries. The roof of anatomical snuff box is formed by skin and flooring by scaphoid and trapezium.
Buy 25 mg promethazine with visa
Stable patient allergy shots oklahoma city promethazine 25 mg cheap with mastercard, unstable pelvis: In this example allergy treatment medication promethazine 25 mg discount mastercard, it is necessary to make the pelvis steady either by exterior or inside fixation, until it heals. Unstable affected person, secure pelvis: Here one must evaluate the cause for hemodynamic instability and deal with the identical. Once the patient is hemodynamically steady then the pelvic harm has to be handled on its deserves. Surgical Procedures According to Location of the Lesion Pelvic injuries are grouped into anterior lesions and posterior lesions. The anterior lesions encompass separation of symphysis or fractures via the rami. The posterior lesions include fracture via the sacrum, fracture dislocation or dislocation through sacroiliac joint or fracture by way of iliac wing. In circumstances of sacroiliac fracture dislocations and fractures, it will require some reduction to achieve the steadiness. In previous, the usage of exterior fixation utilizing pin buy within the iliac wing was considered panacea for stabilizing any kind of pelvic injury. But varied biomechanical studies have proved that external fixator at the most could make grossly unstable fracture into partially steady and will assist in achieving temponade solely in few damage patterns. For sacral fractures, one can select from variety of locking plates, transiliac fixation gadgets or in some circumstances even lumbo-sacroiliac devices. Sacroiliac fixation can be accomplished either utilizing iliosacro screw beneath C arm management or anterior or posterior sacroiliac plating. It is mistaken to assume that exterior fixation alone or plating of symphysis would end in secure pelvis and good outcome. By combining sacroiliac screws with transiliac bars, roughly 90% of intact pelvic stability was achieved. They instructed that rigid posterior fixation of sacroiliac dislocations alone could obviate the need for extra advanced anterior surgical procedures to fix rami fractures. In Tile type C exterior fixation lead to a major larger rate of posterior dislocation than inside fixation. It can be found that external fixation pins placed in dense bone within the supra-acetabular space between anterior superior and anterior inferior iliac spines have better purchase than ones in the iliac crest. Symphysis plating: It has been found that two plates, one on superior side to management vertical shift and one on anterior aspect 1460 TexTbook of orThopedics and Trauma Fixator alongside Iliac Crest I choose 1. Avoid stripping iliacus muscle, as dissection along the inner table might decompress the hematoma, thus losing the temponade effect. After incision, place two K wires, one every on the surface of inner and outer desk to assess the obliquity of the pelvis. Hence the pin must be positioned in the course of the width of the iliac crest, else it will not have good purchase within the bone. The course of the Schanz screw is from head to foot in the path of the stable bone of supra-acetabular space. Use T deal with to insert the screw, feeling the adequacy of purchase within the bone throughout and to keep away from perforation the cortex inadvertently. I normally choose three Schanz screws, starting at a point, 2 cm posterior to anterior superior iliac backbone in the course of the thickest part of the crest and the third screw in the thick part of the crest. Frame assembly: Connect these screws on each hemipelvis with a brief rod and join these brief rods on both facet by one or two lengthy rods, the more the rods one provides, extra could be the steadiness. As mentioned earlier, the exterior fixator can make a grossly unstable pelvis only partially secure. Iliac wing fracture: Fixation with lag screw along the iliac crest and plate(s) on the inside desk provides enough stability. Sacroiliac dislocation: Anatomic discount and fixation either by two plates anteriorly, iliosacral screws, transilial bars or transilial plates all provide good stability. The stability is markedly elevated if these modalities are additional augmented with anterior inside or exterior fixation. Biomechanical research have shown that combination of two plates across symphysis pubis with any type of inner fixation posteriorly provides most stable fixation, whereas anterior exterior fixator with transilial bar provides least stability. Sacral fractures: One can treat these fractures by either transilial rods or plates. Direct fixation using small fragment plates throughout the fracture site is gaining recognition, and primarily useful if one must decompress the sacral nerve roots. Screw in sharp self-tapping Schanz screw from lateral to medial, anterior to posterior course in course of larger sciatic notch. It is preferable to begin on the uninjured side to get the orientation of the lie of pelvis. Since the anterior fixator is finest suited to open book injury, reduction is obtained manually by medial pressure on the displaced hemi pelvis and tightening the clamps securing the rod(s). Symphysis Plating (Indicated for Symphysis Disruption) Preoperative care: Catheterize the bladder; throughout surgery pack the retropubic house with mop to prevent bladder and urethral damage. Position: Supine, one could use radiolucent desk if utilizing picture intensifier to verify overall reduction of pelvis. Approach: Pfannenstiel, in a lot of the instances, but anterior midline approach may be used if laparotomy is being carried out. In open book kind of injury due to anteroposterior force, the affected pubis can be rotated inferolateral. In vertical shear damage it might be rotated superolateral and in lateral compression damage it would be rotated medially. If difficult, one might use following techniques: � Towel clip discount clamp positioned in obturator foramina � Screws in superior or anterior side and using cerclage wire � Screws and pelvic reduction clamp � Longitudinal traction to the limb � External fixator spanning reverse iliac crest and anterior supraacetabular pin with distraction force in lateral compression injuries to disimpact the locked pelvis. These are long screws taking buy in the physique of pubis, often 35 mm or longer. I choose six gap plate with two lateral screws on every superior pubic ramus, as the holes within the centers overlay the vertical screws within the pubis. The length screws must be selected such that they simply penetrate the posterior cortex of pubis, else they may rub in opposition to the bladder even later. Postoperatively, the patient is allowed to turn in bed immediately and allowed partial weight bearing walking because the ache permits, steadily progressing to full weight bearing in 6�8 weeks. A screw from one pubic tubercle to one other across the symphysis offers excellent stability, much like anterior plate fixation. Once the wire is in satisfactory position one can drill cannulated cancellous screw to repair the separation. Pubic rami fractures: Pubic ramus might break subsequent to tubercle, in its midportion or near its attachment to ilium. In the primary two cases, retrograde screw with entry level at pubic tubercle, going into the medullary canal of superior pubic ramus can be used. If the fracture is much too lateral, supra-acetabular screw from lateral to medial is most well-liked.
Buy generic promethazine 25 mg on line
Highspeed motorcar travel allergy testing kingwood tx cheap promethazine 25 mg amex, improved restraint systems like airbags and seat belts allergy symptoms of gluten intolerance 25 mg promethazine buy with mastercard, and improved roadway infrastructure have resulted in an increasing incidence of excessive velocity trauma that confronts the Indian orthopod. While fatalities from excessive power accidents have decreased, the incidence of those extremely extreme injuries is increasing. Due to excessive vitality nature of trauma, pilon fractures are incessantly seen in the polytraumatized affected person. Marked commi nution and displacement, chondral impaction, fibular fractures and articular debris are frequent. Open wounds, bone loss, fracture blisters, and accompanying osseous and gentle tissue devitalization may be present. Each force that causes the fracture imparts its personal specific type of injury, so the direction and price of utility of the injurious pressure, and the place of the foot at the time of loading affect the fracture pattern. Severe compression injuries are sometimes seen in sufferers falling from a peak, whereas shearing accidents are often seen in snowboarding injuries or major motorcar trauma. Most typically, nevertheless, with the complicated drive patterns of highenergy motorcar trauma, a mix of most of these accidents is seen. If the compression fracture has been disimpacted by manipulation, cancellous bone distracts, heals poorly and delays union. Fibula: In many compression accidents, the fibula might remain intact, driving the ankle into varus with extreme impaction of the medial part of the tibial plafond. Minor cracks might appear at the joint surface, with mildly or moderately displaced massive articular fragments and minimal chondral harm. Tibia metaphysis: Shearing forces produce a spiral bony injury, minimal comminution but a disrupted delicate tissue envelope. In spite of severity of swelling, the gentle tissue envelope is injured to a lesser diploma. Also, the intact fibula acts as a post, stabilizing the important lateral aspect of the joint. Impact with the foot in the impartial place leads to central comminution, while a vertical impression on a dorsiflexed foot leads to cephalad and anterior force, with comminution of the anterior plafond. The persona and configuration of the person fracture, is the results of a decision of these forces. Therefore, a spectrum of potential damage exists, depending on the involvement of the articular surface, the metaphysis, and the fibula. Fracture Blisters As the viscoelastic bone is axially loaded in a fast style, it initially absorbs load. However, as the talus continues to be pressured proximally into the distal tibia, the loading forces surpass bone energy, the bone provides way and fractures, dissipating a large amount of vitality to the delicate tissue envelop, much like an internal explosion. Deformation of soppy tissues and inside pressure by bony fragments additional injures the gentle tissue, and manifests as severe swelling, blisters or closed degloving sort injuries. Histologic analysis demonstrated that both fracture blister subtypes represented cleavage injuries at the dermalepidermal junction. The major distinction is the retention of some extent of epidermal cells in the clear blisters, which indicates a superficial harm that reepithelializes quickly. Conversely, the dermis of the bloodfilled subtype is totally freed from epidermal cells, indicative of a deeper injury involving the papillary vascu lature, and which results in elevated reepithelialization time. Although reports in literature concerning fracture blisters and their administration are limited, hemorrhagic blisters seem to be related to elevated complication rates, scarring, and delayed surgical intervention. Several strategies can be used to deal with fracture blisters together with: (i) Sterile unroofing with the applying of Silvadene and/or nonadherent dressings; (ii) Sterile aspiration with maintenance of the overlying roof; and (iii) Leaving the blister intact. We undertake software of silver sulfadiazine after aspiration of blisters to promote therapeutic. If the prognosis for that particular harm is poor, the patient can be so informed preoperatively. This also prevents unrealistic expectations and misunderstandings between the surgeon and the affected person, and inspires religion and belief of the affected person. In closed fractures, pores and skin is assessed for presence of swelling, blisters, stretching, loss of skin wrinkles, strain points as a outcome of displaced bone fragments and hemarthrosis. Compound fractures necessitate detailed examination and documentation for pores and skin loss, bone fragments, neurovascular harm and immediate debridement the place indicated. Gustilo Andersen classification of open fractures helps classify and document severity. Compartment syndrome could develop following a highenergy mechanism, and should always be dominated out. If the scientific indicators of an impending compartment syndrome (pain out of proportion, or ache on passive stretch of the toes) are present, compartment pressures ought to be measured. Compartment pressures should also be measured in the unconscious affected person with a tense, swollen leg. If concerns regarding the vascular integrity of the limb stay, an anklebrachial index should be carried out. If following a mild manipulative reduction, the anklebrachial index stays beneath 0. Tracing and templating the fragment is an age old warhorse that helps to understand configuration and orientation of fracture and plan the placement of lag screws and implant. Oblique Views these views aid in understanding the anatomy of the fracture, extent of bony involvement and displacement into surrounding delicate tissues. They play a significant role in classification of the fracture and its planning the enough management. Stress Views Stress views are helpful to assess ligamentous injury, although not often required or possible. Radiographs ought to be rigorously scrutinized for the quantity, displacement, orientation, comminution and impaction of the fracture fragments. The direction and magnitude of talar displacement, the presence or absence of a fibular fracture and disruptions of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis ought to be seemed for. Interobserver and intraobserver agreements have been proven to be poor with the RuediAllgower system. Most type B fractures have traumatic torsion mechanisms, whereas the Ctype normally have excessive vitality compression mechanisms. Each sort is then additional divided into one of three teams depending on the quantity of fracture comminution. Type A fractures are subdivided into: � Type A1: Extraarticular fracture, metaphyseal simple; � Type A2: Extraarticular fracture, metaphyseal wedge; � Type A3: Extraarticular fracture, metaphyseal complex as shown in the determine beneath. Type B fractures are further subdivided as: � Type B1: Partial articular fracture, pure cut up; � Type B2: Partial articular fracture, splitdepression; � Type B3: Partial articular fracture, multifragmentary depres sion. Type C fractures are additional classified as: � Type C1: Complete articular simple, metaphyseal simple; � Type C2: Complete articular fracture, articular simple, metaphyseal multifragmentary; � Type C3: Complete articular fracture, multifragmentary. The subclassification is complicated, complete and great tool in research, though is poor interobserver reliability stays a concern. The sagittal fracture household was further categorised into T kind, sagittal kind and inverted V sort.