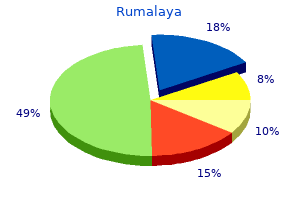
Rumalaya 60 pills order on-line
This wave is as a end result of of treatment depression 60 pills rumalaya purchase amex early systolic stress transmission from the adjacent carotid artery and could also be termed a carotid impact wave medications quetiapine fumarate rumalaya 60 pills buy without a prescription. Central venous strain monitoring is the least invasive methodology, followed by pulmonary artery and left atrial pressure monitoring. Proper interpretation of all cardiac filling pressures requires information of normal values for pressures inside the cardiac chambers, nice vessels, and other measured and derived hemodynamic variables (Table 45-2). The diastolic components (y descent, end-diastolic a wave) and the systolic parts (c wave, x descent, end-systolic v wave) are all clearly delineated. A mid-diastolic plateau wave, the h wave, can be seen because heart fee is slow. Waveform identification is aided by timing the relation between individual waveform components and the electrocardiographic R wave. The x descent can be divided into two parts, x and x, comparable to the segments before and after the c wave. The final atrial strain peak is the v wave, which is brought on by venous filling of the atrium throughout late systole while the tricuspid valve stays closed. Atrial stress then decreases, inscribing the y descent, or diastolic collapse, because the tricuspid valve opens and blood flows from atrium to ventricle. This regular physiologic delay displays the times required for the unfold of the electrical depolarization through the ventricle (60 milliseconds), isovolumic left ventricular contraction (60 milliseconds), transmission of aortic pressure rise to the radial artery (50 milliseconds), and transmission of the radial artery stress rise through fluid-filled tubing to the transducer (10 milliseconds). However, one typically identifies these waves not by their onset or upstroke, but somewhat by the placement of their peaks. In this instance, a and c waves merge, and this composite wave is termed an a-c wave. Although the ascent of the v wave begins during late systole, the height of the v wave happens during isovolumic ventricular relaxation, instantly earlier than atrioventricular valve opening and the y descent. Consequently, the most precise description would be that the v wave begins in late systole, but peaks during isovolumic ventricular leisure, the earliest portion of diastole. It is more helpful to seek for the expected waveform elements, together with these waveforms which are attribute of the pathologic conditions suspected. One of the commonest purposes is the fast prognosis of cardiac arrhythmias. Isorhythmic atrioventricular dissociation or junctional (nodal) rhythm alters the normal sequence of atrial contraction before ventricular contraction. Absence of normal atrioventricular synchrony throughout ventricular pacing could be identified similarly by trying to find cannon waves in the venous strain hint. Note absence of the a wave, a distinguished c wave, and a preserved v wave and y descent. Reduced ventricular filling accompanying this arrhythmia causes a decreased arterial blood strain. Atrioventricular sequential pacing restores the conventional venous waveform and increases arterial blood pressure (right panel). This results in a broad, tall systolic c-v wave, beginning in early systole and obliterating the systolic x descent in atrial pressure. The a wave is unusually outstanding and the y descent is attenuated, owing to the impaired diastolic egress of blood from the atrium. These patterns are interpreted finest along side pulmonary artery pressure monitoring, which is mentioned later. Perhaps the essential scientific query with regard to intravascular quantity responsiveness should be phrased within the negative-that is, whether a affected person is unlikely to respond to an intravenous fluid problem. The subset of sufferers that can undergo all the deleterious effects of fluid administration (capillary leak and tissue edema) and no benefit (increased cardiac output) is in most instances the group of clinical curiosity. Note that this regurgitant wave differs in onset, period, and magnitude from a normal v wave brought on by end-systolic atrial filling from the vena cavae. Unlike tricuspid regurgitation, tricuspid stenosis produces a diastolic defect in atrial emptying and ventricular filling. The third lumen leads to a balloon close to the tip, and the fourth houses wires for a temperature thermistor, the tip of which lies simply proximal to the balloon. Characteristic waveforms recorded during passage of the pulmonary artery catheter. The right atrial strain resembles a central venous pressure waveform and displays a, c, and v waves. Right ventricular pressure shows a higher systolic strain than seen in the proper atrium, though the end-diastolic pressures are equal in these two chambers. Pulmonary artery strain exhibits a diastolic step-up compared with ventricular strain. Note also that right ventricular pressure will increase throughout diastole, whereas pulmonary artery stress decreases during diastole (shaded boxes). Pulmonary artery wedge stress has a similar morphology to proper atrial strain, although the a-c and v waves appear later in the cardiac cycle relative to the electrocardiogram. A large-bore introducer sheath with a hemostasis valve at its outer end is inserted in a fashion much like that for central venous cannulation. The balloon on the tip of the catheter is inflated with air, and the catheter is superior into the best atrium, by way of the tricuspid valve, the best ventricle, the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery, and at last into the wedge place. Characteristic waveforms from each of these areas affirm proper catheter passage and placement. After the pulmonary artery wedge strain is measured, the balloon is deflated, and the pulmonary artery pressure waveform should reappear. Wedge strain may be obtained as needed by reinflating the balloon and permitting the catheter to float distally until pulmonary artery occlusion once more occurs. When different websites are chosen for catheter placement, extra distance is required, usually an extra 5 to 10 cm from the left inner jugular and left and right external jugular veins, 15 cm from the femoral veins, and 30 to 35 cm from the antecubital veins. In these instances, the best internal jugular vein joins the persistent left superior vena cava by a bridging innominate vein. The air-filled balloon tends to float to nondependent regions as it passes via the heart into the pulmonary vasculature. On event, a catheter may be floated to proper place when stiffened by injecting 10 to 20 mL of ice-cold resolution via the distal lumen. Arrhythmias are the primary complication observed throughout pulmonary artery catheterization. Shah and associates noticed transient untimely ventricular contractions in 68% and atrial dysrhythmias in 1. However, the place of the catheter tip ought to all the time be checked by observation of the pressure waveform and chest radiograph to identify catheters that have migrated again into the best ventricle. In these patients, full heart block may be precipitated, though this is uncommon. Shah and associates catheterized 113 patients with preexisting left bundle branch block; only one patient developing complete coronary heart block (0. Although gross structural defects in the catheter itself should be recognized by inspection of the catheter earlier than insertion, extra refined manufacturing issues could escape detection. Knots may be untied by radiologists using intravascular snares and fluoroscopic steering. Procedural errors embrace pointless catheter manipulation, extreme insertion depth, unrecognized persistent wedge stress, extended balloon inflation, or improper balloon inflation with liquid somewhat than air.
Rumalaya 60 pills order otc
An inguinal approach medicine 0027 v rumalaya 60 pills buy lowest price, with needle insertion in the inguinal crease at the midpoint of a line drawn between the internal border of the adductor longus tendon and the femoral arterial pulse has been lately described symptoms bipolar 60 pills rumalaya buy. Along the line, a mark is made at 6 cm inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine, defining the needle insertion website. A 21-gauge, 10-cm, insulated needle is superior in a sagittal aircraft until an evoked motor response is elicited, usually at a depth of 5 to 7 cm from the skin. Once the needle is positioned properly, 20 to 30 mL of local anesthetic is injected slowly and incrementally. Plantar flexion of the foot (tibial nerve component) or dorsiflexion (common peroneal nerve) is an appropriate motor response. Because of the proximal nature of the block, a hamstring motor response additionally is suitable. Classically, the dural sac terminates on the lower border of S2; nonetheless, there are clinical reports of subarachnoid puncture with a 6- to 7-cm caudal needle to counsel individual variations below this "basic" location. Finally, an appreciation of the pelvic contents, especially colon, rectum, and bladder, is essential. Should a deeply inserted needle enter the colon or rectum and never be seen, it may end up in contamination of the sacral canal. Side Effects and Complications Complications are uncommon, however this block is technically tougher than different decrease extremity blocks. This is essentially the most proximal method to the sciatic nerve, and it leads to block of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. The most outstanding aspects of the posterior superior iliac backbone and the ischial tuberosity are identified, and a line is drawn joining these two factors. Needle insertion web site is alongside the road, 6 cm inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine. The sciatic nerve consists of two nerves bound by a typical sheath of connective tissue; the tibial component is medial and anterior, and the common peroneal part is lateral and barely posterior. After passing through the sacrosciatic foramen beneath the piriformis muscle, it lies between the higher trochanter of the femur and the ischial tuberosity. The nerve becomes superficial on the lower border of the gluteus maximus muscle, the place it begins its descent down the posterior facet of the thigh to the popliteal fossa. The nerve provides cutaneous innervation to the posterior facet of the thigh and the entire leg and foot below the knee, except a thin medial strip supplied by the saphenous nerve. This type of anesthesia avoids the sympathectomy related to neuraxial blocks and subsequently could also be advantageous when any shift in hemodynamics could be deleterious, similar to in sufferers with severe aortic stenosis. For the classic (posterior) method of Labat, the patient is positioned laterally, with the leg to be blocked rolled ahead onto the flexed knee as the heel rests on the knee of the dependent nonoperative leg (modified Sims position;. The intersection of this line with the perpendicular line signifies the point of needle entry and falls three to 5 cm along the line. A 22-gauge, 10- to 12-cm needle is superior until a motor response (or paresthesia) is elicited or bone is contacted. Anatomic landmarks for the classic posterior strategy of Labat for sciatic nerve block. If bone is encountered, the needle is redirected medially; if blood is apirated (superior gluteal artery), the needle is redirected laterally. After the needle is placed properly, a complete of 20 to 30 mL of local anesthetic is injected. With this strategy, the affected person is positioned laterally in a modified Sims position; the leg to be blocked is rolled forward onto the flexed knee because the heel rests on the knee of the dependent (nonoperative) leg. This strategy relies on the bony relationship to the greater trochanter and the ischial tuberosity. The most outstanding elements of the higher trochanter and the ischial tuberosity are recognized by palpation, and a line is drawn joining these two factors. The site of the needle insertion can be at the intersection of the two traces or as far as 6 cm distally along the second line. A 21-gauge, 10- to 12-cm needle is inserted perpendicularly and advanced until a tibial or peroneal motor response (or paresthesia) within the ankle or foot is elicited, and 20 to 30 mL of native anesthetic is injected incrementally. If no response is elicited, the needle may be redirected 1 to 2 cm medially or laterally to the unique course of the needle. It could also be helpful to palpate or visualize the groove on the posterior aspect of the thigh. A curvilinear probe is placed just distal to the gluteal cleft and scanned lateral to medial. The sciatic nerve can be identified as a flat hyperechoic struc- ture medial to the larger trochanter and lateral to the hyperechoic border of the ischial tuberosity. The needle is superior in an out-of-plane method in direction of the sciatic nerve (see also Chapter 58). A second line parallel to the inguinal ligament is drawn, beginning on the tuberosity of the higher trochanter. The intersection of this second line with the more medial of the perpendicular strains represents the point of needle entry. The needle is advanced until it contacts bone, the lesser trochanter of the femur. The needle is redirected medially previous the femur, and a paresthesia or nerve stimulator response is sought at a depth of about 5 cm past the bone. A complete of 20 to 25 mL of solution is injected incrementally after careful aspiration. The sciatic nerve can also be blocked with the affected person within the lateral84 and lithotomy positions,eighty five although these are rarely used clinically. Side Effects and Complications Serious problems of sciatic nerve block are rare; nonetheless, theoretical concerns regarding muscle trauma and puncture of a variety of vascular buildings, should be thought-about. On some events, such as limb reimplantations and sympathetically mediated pain circumstances, this sympathetic block could also be advantageous. Thus, thoughtful utility of this system is required to optimize neurologic end result for sufferers thought of to be at high risk of perioperative nerve injury from surgery or preexisting neurologic dysfunction. As these muscular tissues are traced distally from their origin on the ischial tuberosity, they separate into medial (semimembranosus, semitendinosus) and lateral (biceps) musculature, they usually kind the upper border of the popliteal fossa. The decrease border of the popliteal fossa is defined by the 2 heads of the gastrocnemius. In the higher a part of the popliteal fossa, the sciatic nerve lies posterolateral to the popliteal vessels. The popliteal vein is medial to the nerve, and the popliteal artery is most anterior, lying on the popliteal surface of the femur. Near the upper border of the popliteal fossa, the 2 elements of the sciatic nerve separate. The peroneal nerve diverges laterally, and the larger tibial department descends virtually straight down via the fossa. The tibial nerve and popliteal vessels then disappear deep to the converging heads of the gastrocnemius muscle.
Effective rumalaya 60 pills
International HapMap Consortium: A second era human haplotype map of over three medications 2355 generic 60 pills rumalaya with visa. Nekrutenko A medications to treat bipolar cheap rumalaya 60 pills mastercard, Taylor J: Next-generation sequencing data interpretation: enhancing reproducibility and accessibility, Nat Rev Genet 13:667-672, 2012. Kiezun A, Garimella K, Do R, et al: Exome sequencing and the genetic foundation of complicated traits, Nat Genet forty four:623-630, 2012. This fulminant syndrome is elicited by the administration of triggering anesthetic brokers, corresponding to a risky anesthetic or a depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent. Also covered on this chapter are a number of the neuromuscular disorders, although not often encountered in a routine anesthetic apply. This group of problems challenges each perioperative management and intensive care. They affect the normal perform of the peripheral nerves, the neuromuscular junction, and/or muscle tissue. Although such diseases are thought to be rare, the number of sufferers that a clinician might encounter is growing due to higher medical care, rising longevity, and probably other unidentified factors. Neuromuscular issues have a major potential to interact with an improper anesthetic plan, and all affected sufferers require special perioperative attention for anesthetic management. In this space, the armamentarium of invasive and noninvasive diagnostic tools is being developed, especially in genetics. Parallel research in people are restricted by scarce material for scientific research and are sophisticated by the fact that phenotypes within a genotype differ as a result of sex, age, genetic, epigenetic, and environmental modifiers. Porcine stress syndrome,17 which is associated with increased metabolism, acidosis, rigidity, fever, and demise from fast deterioration of muscle and ends in pale, gentle, exudative pork,18 could be triggered by any stress, similar to separation, delivery circumstances, weaning, combating, coitus, or preparation for slaughter, and had turn out to be a big drawback for meat production. Normal muscle contraction is initiated by nerve impulses arriving on the neuromuscular junction. Invaginations of the floor membrane (transverse or T tubules) act as conduits to direct motion potentials rapidly and uniformly deep within the myofibrils the place they transduce a conformational change in the voltage sensor integral to CaV1. The Ca2+ binds to contractile proteins (troponin C and tropomyosin) within the thin filament to expose the myosin-binding sites on actin that activate the thick filament (myosin) and cause a shortening of the muscle fibers. Key ion channels involved in neuromuscular transmission and excitation-contraction coupling. Nerve impulses arriving on the nerve terminal activate voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (1). The resulting enhance in cytoplasmic Ca2+ focus triggers the exocytosis strategy of acetylcholine. Depolarizing the sarcolemma to threshold activates voltage-gated Na+ channels (3), which initiates motion potential impulses that propagate deep into the muscle by way of the transverse tubule system. Within the transverse tubule system, L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels sense membrane depolarization and undergo a conformational change (4). Dantrolene is therapeutic as a outcome of it reduces the concentration of sarcoplasmic Ca2+. However, the pathway by which dantrolene lowers sarcoplasmic Ca2+ is advanced and still not fully understood. This physical interaction engages a type of bidirectional signaling that tightly regulates the function of both proteins. This dysregulation can be observed in vitro as heightened sensitivity to volatile anesthetics, 4-chloro-m-cresol, caffeine, ryanodine, and potassium depolarization. First, Ca2+ activates the channel in a graded method between 100 nM and a hundred M, whereas larger concentrations inhibit channel activity. It is probably going that Mg2+ acts by competing with Ca2+ at its activator websites and by binding to yet unidentified low-affinity inhibitory sites. Therefore hypersensitivity to pharmacologic brokers is more doubtless to be carefully tied to altered responses to physiologic ligands. Physiologic characterization of the mutation additional demonstrated that sensitivity of RyR1 exercise is considerably enhanced by membrane depolarization or by pharmacologic activators of RyR1. Nonetheless, R174W-expressing myotubes have a chronic elevation of free sarcoplasmic resting Ca2+ and an elevated sensitivity of Ca2+ launch to caffeine and halothane, compared with myotubes expressing wild-type CaV1. This outcome instructed an in depth relationship between practical neurochemical transmission throughout the neuromuscular junction or depolarization of the sarcolemma (or both) and the clinical syndrome. Paul-Pletzer and associates demonstrated that [3H] azidodantrolene specifically labels the amino terminus of RyR1 outlined by the 1400�amino acid residue N-terminal calpain digestion fragment of RyR1. Some mutations appear to be clustered in a given area of the world, however the distribution and frequency appear to be considerably population specific. Schematic illustration of the triadic junction of skeletal muscle reveals the junctional foot protein (ryanodine [Ry1] receptor) and its associated proteins. These physical hyperlinks transmit important indicators throughout the slender gap of the triadic junction that activate the Ry1 receptor and launch Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The lowest concentration of caffeine that produces a sustained enhance of at least 0. Then the halothane threshold is obtained using the identical methodology by exposing the muscle to halothane concentrations of zero. The dynamic halothane take a look at is performed with the muscle stretched at a constant rate of four mm/min to obtain a drive of roughly 3 g and held on the new length for 1 minute after a 3-minute exposure to halothane. Optional tests include publicity of muscle to a combination of each 1% halothane and incremental caffeine concentrations and to 2% halothane alone. Data collaboration of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Thomas Jefferson University, Wake Forest University, University of California, Davis, and Barrow Neurological Institute. Thus the onset of the syndrome in people is extremely variable each in preliminary symptoms and within the time of onset of the syndrome. Its onset is so variable that making the prognosis in the setting of a medical anesthetic could be quite difficult. Rigidity after induction with succinylcholine but successful intubation, followed rapidly by the symptoms listed after scenario 2 2. It can be delayed for several reasons and is probably not overt till the affected person is in the recovery room. Stresses associated with these episodes include exercise and environmental exposure to risky nonanesthetic vapors. In some sufferers, this improve is average; in a very few, the effect is extreme. Muscle ultrasound usually demonstrates elevated echogenicity within the quadriceps muscle with relative sparing of the rectus muscle. The masseter and lateral pterygoid muscle tissue contain slow tonic fibers that can respond to depolarizing neuromuscular blockers with a contracture. This jaw rigidity might happen even after pretreatment with a defasciculating dose of a nondepolarizing relaxant. However, in additional than 80% of patients with trismus but no rigidity of different muscular tissues. These indicators must be distinguished from different issues with related signs (Box 43-2).
60 pills rumalaya free shipping
The tubes are straight medications similar to abilify rumalaya 60 pills purchase without a prescription, wire-reinforced treatment quadriceps pain 60 pills rumalaya purchase mastercard, and have a soft molded tip designed to prevent impingement on laryngeal structures. Aintree intubating catheter within a versatile intubation scope, inserted by way of a laryngeal masks airway. The information is usually a steel guidewire, though an epidural catheter can be utilized. The anterior neck should be cleansed earlier than puncture, and aseptic technique should be used. The translaryngeal puncture web site could be performed superior or inferior to the cricoid Chapter 55: Airway Management within the Adult 1677 cartilage. At this stage, reconfirmation of a place within the trachea and instillation of a local anesthetic may be carried out with a second syringe filled with 2 to 4 mL of 2% or 4% lidocaine. The guidewire is then advanced through the angiocatheter until it exits the mouth or nostril. The guidewire is clamped with a hemostat at the level of the pores and skin of the neck to prevent migration. Potential complications embody bleeding (usually minimal), subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, and harm to the posterior trachea or esophagus. B, the information catheter is threaded over the guidewire till it contacts the laryngeal access website. C, After advancing the information catheter 2 to three cm, the endotracheal tube is advanced into the trachea. They are designated as left sided or proper sided, depending on whether or not the bronchial lumen goes to the left or right main bronchus. The blue bronchial cuff should be positioned slightly below the carina in the acceptable bronchus. Inflation of the blue bronchial balloon underneath direct visualization helps confirm correct placement. Bronchial blockers are basically hole, balloontipped catheters which are endobronchially placed to isolate and deflate one lung. In these situations, the usage of a modified singlelumen tube with an built-in bronchial blocker. They can also be used as a major airway in some difficult airway situations when attempts at securing a noninvasive airway are likely to fail, such as a patient with a laryngeal neoplasm and important airway obstruction. Expiration is passive on account of the elastic recoil of the lungs and the chest wall. Allowing adequate time for passive expiration to keep away from barotrauma from breath stacking is imperative. Expiration occurs through the glottis and is determined by a nonobstructed upper airway, which is crucial to keep away from barotrauma and ensuing pneumothorax. Confirmation of proper intratracheal placement of the catheter by testing for aspiration of air is crucial before initiating jet ventilation. The pipeline strain for oxygen in hospitals within the United States is roughly fifty five psi. Commercially obtainable jet ventilators generally include stress regulators to decrease the pipeline stress to provide profitable jet air flow while avoiding higher pressures which may end in barotrauma. In most situations within the operating room, adequate pressure for jet air flow could be achieved by connecting straight to the pipeline provide. To stop this complication, ensuring that a path for air egress exists and that enough time for passive expiration is on the market is an absolute necessity. The lowest possible stress that can present enough oxygenation and air flow should be used. Cricothyrotomy tools ought to be included in all emergency airway storage units and readily available. Other contraindications to cricothyrotomy embody laryngeal fractures, laryngeal neoplasm, subglottic stenosis, coagulopathy, and distorted or unidentifiable neck anatomy. The two most common techniques for performing a cricothyrotomy are the percutaneous dilational cricothyrotomy and the surgical cricothyrotomy. For the anesthesiologist, the percutaneous technique is normally preferred as a end result of the method is simpler in contrast with a surgical cricothyrotomy, and because of the familiarity of utilizing the Seldinger method for other procedures. The foundation for this process is the insertion of an airway catheter over a dilator that has been inserted over a guidewire. An 18-gauge needle-catheter connected to a fluidfilled syringe is passed through the incision at a 45-degree angle in the caudal direction with continuous aspiration. The catheter is removed, and the curved dilator with the airway cannula is threaded over the guidewire. The dilator and guidewire are eliminated collectively while the cannula stays in place. Proper placement is confirmed by capnography, and the airway cannula is secured in place. The access level for percutaneous cricothyrotomy is within the lower third of the cricothyroid membrane. This technique is probably the most rapid and must be used when equipment for the much less invasive methods is unavailable and pace is particularly essential. Placement of the airway cannula within the subcutaneous tissue can lead to subcutaneous or mediastinal emphysema. Late complications from cricothyrotomy include swallowing dysfunction, an infection, voice modifications, and tracheal stenosis. Tracheal stenosis has an incidence of approximately 2% to 8% in adults and is extra probably if preexisting trauma or infection is current. Although appreciable emphasis is placed on the issues that can come up throughout induction and intubation, the risk for issues can potentially be more frequent throughout extubation of the trachea. Failed extubation may finish up from the failure of oxygenation, failure of ventilation, insufficient clearance of pulmonary secretions, or lack of airway patency. As such, the anesthesia practitioner needs to stratify the extubation risk preemptively and establish an extubation plan earlier than attempting extubation. The awake patient can more easily keep a patent airway, attributable to the recovery of awake pharyngeal muscle tone and airway reflexes. Deep extubation avoids coughing and adverse hemodynamic effects but risks upper airway obstruction and hypoventilation. General preparations for extubation ought to embrace ensuring enough reversal or recovery from neuromuscular blockade, hemodynamic stability, normothermia, and adequate analgesia. Patients ought to be preoxygenated with a 100 percent fraction of impressed oxygen concentration (Fio2), and alveolar recruitment maneuvers ought to be considered if acceptable. Suctioning of the pharynx (and the trachea, if indicated), the elimination of throat packs, and the location of a chew block should be performed whereas the affected person is beneath deep anesthesia. Patients in whom mask air flow with excessive pressures is important ought to have an orogastric tube positioned and suctioned before extubation. The sniffing place is the standard position for extubation; its major advantage is that the patient is optimally positioned for airway management, if essential.
Discount 60 pills rumalaya overnight delivery
This definition takes under consideration that entire blood saved for 1 hour is far different from that stored for 5 days medicine dispenser discount rumalaya 60 pills line. However treatment 4s syndrome rumalaya 60 pills on line, this quite liberal definition of fresh blood is based on being saved for lower than 5 days. For example, blood stored for less than 24 hours is far completely different than that stored for four days. The degree to which contemporary blood regains its various features is immediately related to the length of storage and whether it has been cooled. The longer blood is saved, the much less efficient it becomes, particularly relating to coagulation. Even 1 unit of whole blood stored for 24 hours at 4� C has less hemostatic results than 1 unit of contemporary blood stored for less than 6 hours because of decreased platelet aggregability. Some institutions define it as recent if it has been stored lower than forty eight hours at 2� to 5� C. The distinction between 1 hour and a pair of days of storage is large, particularly as it pertains to platelet exercise. Numerous articles seem within the literature regarding the usage of fresh complete blood. Part of the reason of variability among studies is related to the duration of storage and use of hypothermia during the storage of fresh whole blood. My expertise in Vietnam verified that typed and crossmatched heat whole blood was extremely effective in treating the coagulopathy from huge transfusions, particularly within the absence of sepsis. Unfortunately, each group mechanically acquired platelets, making any conclusions regarding platelets inconceivable. Not surprisingly, fresh complete blood is efficient in treating unresponsive life-threatening hemorrhage. Basically, administration of older saved blood, colloids, and crystalloids dilute the platelets leading to dilutional thrombocytopenia. After 15 to 20 items of blood have been given, the thrombocytopenia will cause a coagulopathy on a dilutional basis. A more present rule of thumb is to transfuse 1 apheresis pack (6 units) of platelets in anticipation of a platelet count of fifty to 75,000/L. This question was studied within the armed forces when given to massively transfused army sufferers. No difference was present in antagonistic effects and mortality between patient teams receiving platelets. Of course, administration of blood products is only one part of a complete approach to such pressing medical challenges (see additionally Chapters 81 through 83). The following recommendations are temporary and common, with the details of those additional discussed in other sections of this chapter or in other chapters of this edition. The Myberg article "Resuscitation Fluids" states, "Although albumin has been determined to be protected to be used as a resuscitation fluid in most critically sick sufferers and may have a job in early sepsis, its use is related to elevated mortality amongst sufferers with acute mind damage (also see Chapter 70). In sure severe cases, the issues of massive transfusion must be anticipated. As indicated in this chapter, fresh entire blood should be thought-about if out there. For example, storing blood in an electrostatic field of 500 to 3000 V decreases hemolysis and attenuates the decrease in pH related to prolonged storage. An increase in the circulating purple cell mass produces an increase in O2 uptake within the lungs and a corresponding probable increase in O2 delivery to tissues. This is reflected in the sigmoid form of the curve, which signifies that a lower in Pao2 makes considerably extra O2 obtainable to the tissues. The sigmoid shape of the curve implies higher effectivity of blood transportation of O2 from the lungs to tissues. Shifts within the O2 dissociation curve are quantitated by the P50, which is the partial strain of O2 at which Hb is half saturated with O2 at 37� C and pH 7. A low P50 signifies a left shift within the O2-dissociation curve and an increased affinity of Hb for O2; in different words, the left Chapter 61: Patient Blood Management: Transfusion Therapy 1843 shift of the curve signifies that a lower-than-normal O2 tension saturates Hb in the lung and the subsequent release of O2 to the tissues happens at a decrease than normal capillary O2 rigidity. An elevated affinity may be sufficient to ensure that O2 is released to the tissues unless the tissue Po2 is within the hypoxic range. The clinical evidence supporting the accuracy of this speculation during infusion is mentioned in the following part. In 1993, Marik and Sibbald100 found that the administration of blood that had been stored for greater than 15 days really decreased intramucosal pH, suggesting that splanchnic ischemia had occurred. Various protocols have been developed for approaches to massive blood transfusion administration. This coagulopathy is caused by a combination of factors, of which crucial are the quantity of blood given and the length of hypotension or hypoperfusion. Clinical manifestations embody oozing into the surgical area, hematuria, gingival bleeding, petechial bleeding from venipuncture sites, and ecchymosis. For entire blood at a storage temperature of 4� C, platelets are broken sufficiently to be readily trapped and absorbed by the reticuloendothelial system soon after infusion. Considering survival time and viability, complete platelet exercise is simply 50% to 70% of the unique in vivo activity after 6 hours of storage in bank blood at 4� C. After 24 or 48 hours of storage, platelet activity is just roughly 10% or 5% of normal, respectively. Infusion of financial institution blood stored for longer than 24 hours dilutes the available platelet pool. Platelet counts decreased to less than a hundred,000/mm3 when 10 to 15 items of blood got to acutely wounded, previously healthy troopers. One trauma group even suggested that a traditional platelet depend is most likely not excessive enough in severely injured trauma sufferers. The previous paragraph places emphasis on dilutional thrombocytopenia being the main cause of clinical bleeding in sufferers receiving a number of units of blood. In this situation, the clinician can dependably predict what the platelet count might be. Routine monitoring of coagulation (see later discussion) ought to be a normal approach when hemorrhage happens. Although major emphasis had been placed on monitoring the platelet count, several investigators103,104 have questioned the function of dilutional thrombocytopenia in the coagulopathy of massively transfused sufferers. They accurately point out that the platelet count rarely decreases to as low a stage as can be predicted from dilution alone. This is probably as a end result of platelets are released into the circulation from the spleen and bone marrow and because of the presence of nonfunctional platelets. This algorithm for diagnosing and treating an enormous transfusion was modified from the large transfusion protocol used on the San Francisco General Hospital. Platelet remedy could be acceptable in this scenario (see later part on platelet concentrates). Levy and colleagues107 supplied a superb scholarly review of fibrinogen and hemostasis. As indicated earlier, more exact monitoring with thromboelastometry has allowed rather more info to turn into available regarding fibrinogen.
60 pills rumalaya cheap overnight delivery
Ant tib medications covered by medicare generic rumalaya 60 pills without prescription, M tibialis anterior; gast keratin treatment buy rumalaya 60 pills with mastercard, m gastrocnemius; L, left; quad, m quadriceps femoris; R, proper; then, thenar. Although tons of of such case reports exist within the literature, as nicely as many in our experience, the cost effectiveness of such monitoring is unclear. Immediate angiography revealed acute carotid occlusion and completely modified the operation performed on this patient, who recovered utterly. Changes in amplitude were variable until extremely low hematocrit values (7%) had been reached, at which level the amplitude of all waveforms decreased. First, the pathway at risk in the course of the surgical procedure have to be amenable to monitoring. Second, if proof of damage to the pathway is detected, some intervention must be possible. If the data have a high diploma of variability within the absence of scientific interventions, their utility for detecting clinically significant occasions is limited. This chapter critiques the most common clinically used intraoperative neurologic displays. Ideally, clinical research would offer outcome knowledge on the efficacy of a neurologic monitor in a given procedure to enhance neurologic end result. Although a wealth of medical expertise exists with many of these monitoring modalities, little is available in the method in which of randomized potential research evaluating the efficacy of neurologic monitoring. Based on medical experience with neurologic monitoring and nonrandomized clinical studies by which neurologic monitoring is used and customarily in contrast with historic controls, practice patterns for use of neurologic monitoring have developed. In sure procedures, neurologic monitoring is really helpful and used by most facilities; in other procedures, monitoring is used almost routinely in some centers, but not in others; and in some procedures, no clear clinical expertise or proof signifies that monitoring is beneficial at all (experimental use). Finally, in some procedures, monitoring is used selectively for sufferers believed to be at higher than usual risk for intraoperative neurologic injury. In Niedermeier E, Lopes da Silva F, editors: Electroencephalography, ed 5, Philadelphia, 1994, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, p 769. In Gordon E, editor: A foundation and apply of neuroanesthesia, New York, 1981, Elsevier, p three. Skyhoj Olsen T, Larsen B, Bech Skriver E, et al: Focal cerebral ischemia measured by the intra-arterial 133Xe technique: limitations of two-dimensional blood move measurements, Stroke 12:736-744, 1981. Ostergaard L: Cerebral perfusion imaging by bolus monitoring, Top Magn Reson Imaging 15:3-9, 2004. White H, Baker A: Continuous jugular venous oximetry within the neurointensive care unit: a quick review, Can J Anaesth 49:623-629, 2002. Hongo K, Kobayashi S, Okudera H, et al: Noninvasive cerebral optical spectroscopy: depth-resolved measurements of cerebral haemodynamics using indocyanine green, Neurol Res 17:89-93, 1995. Vajkoczy P, Horn P, Thome C, et al: Regional cerebral blood move monitoring in the prognosis of delayed ischemia following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, J Neurosurg 98:1227-1234, 2003. Vajkoczy P, Roth H, Horn P, et al: Continuous monitoring of regional cerebral blood circulate: experimental and medical validation of a novel thermal diffusion microprobe, J Neurosurg ninety three:265-274, 2000. Longhi L, Pagan F, Valeriani V, et al: Monitoring mind tissue oxygen pressure in brain-injured patients reveals hypoxic episodes in normal-appearing and in perifocal tissue, Intensive Care Med 33:2136-2142, 2007. Implications for trials of ancillary strategies, Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 23:117-126, 2002. Brauer P, Kochs E, Werner C, et al: Correlation of transcranial Doppler sonography mean move velocity with cerebral blood move in patients with intracranial pathology, J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 10:80-85, 1998. Bundo M, Inao S, Nakamura A, et al: Changes of neural exercise correlate with the severity of cortical ischemia in patients with unilateral main cerebral artery occlusion, Stroke 33:sixty one, 2002. Symon L: Flow thresholds in mind ischaemia and the consequences of medicine, Br J Anaesth 57:34, 1985. Ganes T: A study of peripheral, cervical, and cortical evoked potentials and afferent conduction occasions within the somatosensory pathway, Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 49:446, 1980. Sasaki T, Itakura T, Suzuki K, et al: Intraoperative monitoring of visible evoked potential: introduction of a clinically useful methodology, J Neurosurg 112:273-284, 2010. Szelenyi A, Bueno de Camargo A, Flamm E, et al: Neurophysiological criteria for intraoperative prediction of pure motor hemiplegia throughout aneurysm surgical procedure: case report, J Neurosurg 99:575, 2003. Pelosi L, Lamb J, Grevitt M, et al: Combined monitoring of motor and somatosensory evoked potentials in orthopaedic spinal surgery, Clin Neurophysiol 113:1082, 2002. Ogasawara K, Suga Y, Sasaki M, et al: Intraoperative microemboli and low middle cerebral artery blood circulate velocity are additive in predicting development of cerebral ischemic events after carotid endarterectomy, Stroke 39:3088-3091, 2008. Mueller M, Behnke S, Walter P, et al: Microembolic indicators and intraoperative stroke in carotid endarterectomy, Acta Neurol Scand ninety seven:110-117, 1998. Calderon-Arnulphi M, Alaraj A, Amin-Janjani S, et al: Detection of cerebral ischemia in neurovascular surgical procedure utilizing quantitative frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy, J Neurosurg 106: 283-290, 2007. Mizoi K, Yoshimoto T: Intraoperative monitoring of the somatosensory evoked potentials and cerebral blood circulate during aneurysm surgery: security analysis for momentary vascular occlusion, Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 31:318, 1991. Misoi K, Yoshimoto T: Permissible temporary occlusion time in aneurysm surgical procedure as evaluated by evoked potential monitoring, Neurosurgery 33:434, 1993. Beghi E, Tonini C: Surgery for epilepsy: assessing proof from observational studies, Epilepsy Res 70:97-102, 2006. Kuzniecky R, Devinsky O: Surgery perception: surgical administration of epilepsy, Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:673-681, 2007. In Niedermeier E, Lopes da Silva F, editors: Electroencephalography, ed 5, Philadelphia, 1994, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, pp 769-775. Ramnarayan R, Mackenzie I: Brain-stem auditory evoked responses during microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: predicting postoperative listening to loss, Neurol India 54:250-254, 2006. Brock S, Scaioli V, Ferroli P, Broggi G: Neurovascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia: function of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring within the learning period, Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 82:199-206, 2004. Khrais T, Sanna M: Hearing preservation surgery in vestibular schwannoma, J Laryngol Otol 120:366-370, 2006. Skippen P, Seear M, Poskitt K, et al: Effect of hyperventilation on regional cerebral blood circulate in head-injured youngsters, Crit Care Med 25:1402, 1997. Imberti R, Bellinzona G, Langer M: Cerebral tissue Po2 and Sjvo2 adjustments during average hyperventilation in patients with extreme traumatic mind damage, J Neurosurg 96:97, 2002. Aaslid R: Transcranial Doppler evaluation of cerebral vasospasm, Eur J Ultrasound sixteen:three, 2002. Mascia L, Fedorko L, ter Brugge K, et al: the accuracy of transcranial Doppler to detect vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, Intensive Care Med 29:1088, 2003. Alexandre A, Rubini L, Nertempi P, Farinello C: Sleep alterations during post-traumatic coma as a possible predictor of cognitive defects, Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 28:188-192, 1979. Facco E, Munari M, Baratto F, et al: Multimodality evoked potentials (auditory, somatosensory and motor) in coma, Neurophysiol Clin 23:237-258, 1993. Fandino J, Stocker R, Prokop S, et al: Cerebral oxygenation and systemic trauma associated elements determining neurological consequence after brain damage, J Clin Neurosci 7:226-233, 2000.
Rumalaya 60 pills buy cheap
To keep this focus gradient within the thick ascending limb medications 24 rumalaya 60 pills low price, high-energy demand treatment 3 nail fungus generic 60 pills rumalaya amex. Factors necessary to enable countercurrent trade and to create a urea gradient conspire to make regular medullary partial stress of oxygen (Po2) very low. The descending vasa recta are vasoactive arteriolar microvessels which are anatomically positioned to regulate complete and regional blood move to the outer and internal medulla. A, the inner construction of the kidney includes the vasculature, cortex and medulla areas, and urinary tract constructions. C, the glomerulus is the site where plasma filtration occurs; approximately 20% of plasma coming into the glomerulus will move by way of the specialized capillary wall into the Bowman capsule and enter the tubule to be processed and to generate urine. D, the vascular anatomy of the kidney is very organized, and the medullary microcirculation is a part of the mechanism that allows countercurrent trade. Tightly regulated through tubular processing are extracellular solutes, including sodium, potassium, hydrogen ion, bicarbonate, and glucose. The kidney additionally generates ammonia and eliminates metabolic and nitrogenous wastes, including creatinine, urea, and bilirubin, in addition to toxins and many classes of medication. Finally, the kidneys generate glucose and secrete circulating hormones that influence erythrocyte technology, systemic blood strain, and calcium homeostasis. High concentrations of aldosterone stimulate the reabsorption of sodium and water, primarily within the distal tubule and collecting ducts. Aldosterone is produced by the adrenal cortex in response to the suggestions from the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, simplified as follows. Reduced delivery of sodium to the macula densa causes release of renin from the granular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus. It decreases systemic blood stress by stress-free vascular easy muscle, lowering sympathetic stimulation, and inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. The kidney also synthesizes prostaglandins, which regulate the affect of different hormones. Interaction among the urinary bladder, the kidney, and the ureters influences urine production. Drugs that primarily act on adrenergic receptors tend to stimulate ureteral exercise, whereas agents that primarily activate adrenergic receptors are inclined to inhibit ureteral exercise. In people, irregular peristaltic contractions may happen with retroperitoneal inflammation resulting from appendicitis and peritonitis. Two thirds of the remaining tubular contents are extra sluggishly reabsorbed in the loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule. Finally, extra water is reabsorbed from the remaining effluent within the accumulating ducts (5 to 10 mL per hour) because it passes to larger urine accumulating constructions (1 to 2 mL per minute). Other sources of renal insult in selected patients could embrace rhabdomyolysis and specific drug-related effects. Ischemic renal failure related to shock or extreme dehydration is always preceded by an early compensatory section of normal renal adaptation. Mechanism for renal sodium and volume regulation in response to decreased extracellular quantity. As ischemia persists, the supply of glucose and substrates continues to lower; glycogen is consumed, and the medulla, which depends to a fantastic extent on glycolysis for its vitality sources, turns into more adversely affected. Early cell modifications are reversible, such because the swelling of cell organelles, especially the mitochondria. As ischemia progresses, a scarcity of adenosine triphosphate interferes with the sodium pump mechanism, water and sodium accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum of tubular cells, and the cells start to swell. Onset of tubular injury often occurs within 25 minutes of ischemia because the microvilli of the proximal tubular cell brush borders begin to change. Within an hour, they slough off into the tubular lumen, and membrane bullae protrude into the straight portion of the proximal tubule. After a couple of hours, intratubular stress rises, and tubular fluid passively backflows. Surgery + genetic background Intraop acute kidney harm Postop acute kidney harm Net renal impairment 2. The normal physiologic function of the kidney includes a position of adrenergic receptors in modulating vasoconstrictor (alpha 1) and vasodilating (alpha 2) results, respectively. Rodgers and colleagues carried out a systematic evaluate of 107 randomized medical trials of intraoperative neuraxial blockade and demonstrated a 30% discount in the odds of postoperative mortality. Unfortunately, renal failure was not an end result of a recently printed meta-analysis centered on epidural anesthesia throughout cardiac surgical procedure. However, 43% of volunteers receiving sevoflurane had plasma fluoride levels that exceed 50 m/L. Other explanations for the variations within the renal effects of unstable anesthetics have been sought, together with an evaluation of variation in nephrotoxic compounds generated when an inhaled anesthetic interacts with carbon dioxide absorbents. In breathing circuit systems at a excessive temperature and low move charges, carbon dioxide absorbents degrade sevoflurane, creating fluoromethyl2,2-difluoro-1-(trifluoroethyl) vinyl ether, also identified as compound A. Metabolism of compound A happens by way of conjugation within the liver with glutathione after which modification in the kidney by an enzyme (cysteine-S-conjugate -lyase). Humans have 10- to 30-fold much less renal -lyase enzyme activity compared with rats, which may account for the absence of kidney harm from sevoflurane in people. One study67 compared the protection of low-flow sevoflurane and isoflurane anesthesia in sufferers having extended surgeries (>6 hours). The likely concentrations of compound A possible with sevoflurane during anesthesia have been studied Chapter fifty two: Renal Function Monitoring 1589 in human volunteers. Compound A ranges approached 50 ppm, and 24-hour urine collections have been analyzed for 3 consecutive days after exposure. A multicenter study70 involving seventy three elective surgical procedures lasting 2 to 8 hours in contrast the protection and efficacy of low move (<2 L/min) sevoflurane to isoflurane. Fresh carbon dioxide absorbent was used for all circumstances, and nitrous oxide was not permitted. No variations were present in urine albumin, glucose, protein, or osmolality between therapy groups. In a small research of patients present process cardiac surgical procedure, preconditioning with sevoflurane decreased biochemical markers for renal (and myocardial) dysfunction. Even with decreased glomerular perfusion, a collection of compensatory mechanisms can still protect renal filtration. At a given stage of cardiac output, intrarenal components affect the ratio of renal-to-systemic vascular resistance, thereby influencing the fraction of cardiac output received by the kidneys. At the glomerular capillary, plasma is separated right into a protein-free ultrafiltrate and a nonfiltered portion. Initially, the filtration fraction is maintained by efferent arteriolar constriction. However, if unabated, the mechanisms that influence efferent arteriolar vasoconstriction may finally affect afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction. Most susceptible to the imbalance are the thick ascending tubular cells of the loop of Henle within the medulla. In some cases, the return of perfusion to the cortex has correlated with a return of renal function.

